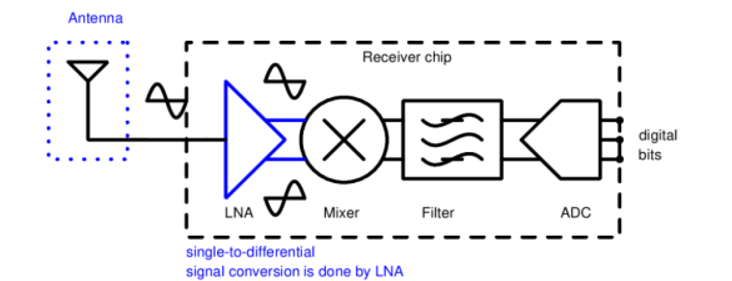
A compact, energy-saving signal amplifier that fits on a small chip and boosts weak radio signals with very little added noise. It uses a single, clever transformer to turn a one-ended input into two balanced outputs, replacing several bulky parts. Computer models show it delivers clear, powerful signals while drawing minimal battery power.
Modern wireless devices, like mobile phones and smart gadgets, need small and power-efficient components to receive signals clearly. One important component is an amplifier that boosts weak signals. Existing designs often require bulky parts and consume a lot of power, making devices larger and draining battery life faster. There is also a need to reduce noise and interference without increasing cost or space.
- Integrated Transformer Architecture: This amplifier merges seven separate coils into one nine-port transformer, saving two-thirds of the chip area.
- On-Chip Single-to-Differential Conversion: This design converts a single input signal into two perfectly balanced outputs without any extra part, boosting noise immunity.
- Current-Reuse Power Saving: This product reuses electric current through paired transistors to cut power use by more than half.
- Superior Signal Linearity: This feature delivers very high signal clarity, handling strong and weak signals together with minimal distortion.
- Ultra-Low-Voltage Operation: This amplifier operates on under 1 V and consumes just 3.4 mW, making it ideal for battery-powered gadgets.
The amplifier circuit was laid out in 65 nm CMOS design software, and its transformer was modeled with electromagnetic tools. Post-layout extraction fed back into circuit simulators, confirming gain, noise, and linearity targets. Physical silicon has been built, and chip measurements are in progress.
The design has been fully developed and tested using computer simulations and modeling tools in a lab setting. It shows excellent results in terms of performance, power use, and size efficiency.
4
By dramatically reducing both the physical footprint and the energy draw of radio amplifiers, this technology makes it possible to build truly pocket-sized wireless gadgets that run for days or even weeks on a single charge. Imagine fitness trackers or smart glasses you never have to plug in, or medical implants that monitor vital signs continuously without frequent battery replacements. In remote villages, solar-powered weather stations and water- quality sensors could operate reliably year-round, giving communities real-time data and saving them costly and time-consuming trips for maintenance. At the same time, shrinking the chip area means using fewer raw materials and cutting back on manufacturing energy, helping electronics makers lower their carbon footprint and bring affordable, eco-friendly connectivity to more people worldwide.
- Smartphones and wearables
- IoT sensor networks
- Wireless medical devices
- Satellite and aerospace radios
- Defence communication systems
- Next-generation network infrastructure
- Consumer electronics
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202421008765
554016