The present invention in general pertains to systems and methods for measuring the dynamic properties of scattering particles within a medium, including fluid flow. Specifically, the present invention relates to systems and methods for high density diffusing wave spectroscopy (DWS). The present invention provides systems and methods for determining dynamics in a target medium or a sample, by measuring a high- density intensity autocorrelation of the sample using a capturing device. The present invention provides systems and methods for determining dynamics in a target medium or sample such as but not limited to flow or viscoelastic properties of the target medium or sample.
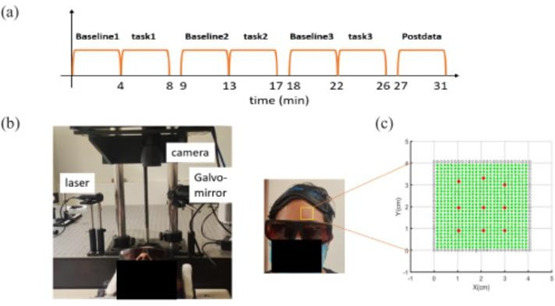
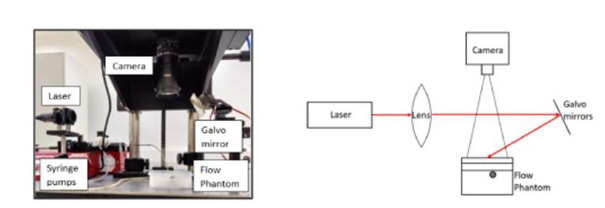
Figure (1) Experimental setup for tomographic imaging of blood flow in prefrontal cortex: (1a) protocol timeline, (1b) M-DCT set-up for the experiment and (1c) sources and detectors indicated by red and green dots respectively; (2) Experimental setup for flow reconstruction using two different flow rates at different layers in a 3-layer phantom.
Conventional diffusing wave spectroscopy (DWS) systems rely on expensive, high-speed detectors and cameras, limiting accessibility and spatial resolution. Low-cost methods using low frame rate cameras often produce inaccurate results due to sensor noise and cannot directly measure the essential intensity autocorrelation function. There is a need for an affordable system that can accurately compute intensity autocorrelation using low frame rate cameras and support both surface and deep tissue measurements with adaptable light source configurations, overcoming current limitations in cost, noise sensitivity, and measurement density.
- Use of Low Frame Rate Cameras for DWS: Unlike conventional diffusing wave spectroscopy systems that rely on expensive, high-speed detectors (APDs, PMTs) and hardware correlators, this technology employs inexpensive CCD/CMOS cameras with low frame rates. This significantly reduces cost and complexity.
- Multi-Exposure Technique and Volterra Integral Equation Inversion: The novel method captures scattered intensity or speckle contrast at multiple exposure times, then mathematically solves a Volterra integral equation of the first kind using Tikhonov regularized least squares.
- High Spatial Density Measurements: Each pixel of the camera acts as an independent detector, enabling simultaneous acquisition of high-density, spatially resolved autocorrelation data over the sample area. This provides detailed insight into spatial variations of dynamic processes within the medium.
- Noise and Gradient Corrections: The system corrects for shot noise and intensity gradients to improve measurement accuracy.
- Flexible Illumination Options: The use of beam shaping optics allows either focused or uniform illumination, enhancing adaptability to different sample types and measurement conditions.
- Non-invasive and Real-time Capability: Suitable for monitoring dynamic properties such as blood flow non-invasively, potentially enabling real-time diagnostics.
The prototype consists of a coherent laser diode light source with beam shaping optics to provide focused or uniform illumination of the sample. Scattered light is captured by a low frame rate CMOS or CCD camera with a high-quality objective lens, enabling high-density speckle data collection over a small area. Multi-exposure control allows capturing intensity data at various exposure times. A microprocessor processes this data using numerical methods to solve the Volterra integral equation, recovering the intensity autocorrelation function. The system features a user interface for easy operation and includes vibration isolation to ensure accurate, non-invasive measurements of dynamic sample properties.
Testing and validation has been done on small animals and humans. Results have been communicated on peer-reviewed journals.
5
This technology makes advanced medical diagnostics more affordable and accessible by lowering the cost of diffusing wave spectroscopy (DWS), enabling non-invasive monitoring of blood flow and tissue dynamics, especially in resource-limited settings. It supports continuous, real-time flow measurements to improve patient management and provides a cost-effective tool for research in soft matter physics, biological tissues, and materials science. Using widely available imaging components broadens access to advanced optical techniques, fostering innovation and better healthcare globally.
- Biomedical and healthcare
- Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology
- Optical Instrumentation and sensor development
- ndustrial process monitoring
Geography of IP
Type of IP
201921036704
562924