Eugenol-Based Composition for Prevention, Treatment and Management of Psoriasis, Process of Synthesis and Applications Thereof
The invention provides a novel nail enamel composition with photoactivated antibacterial and antifungal properties to treat onychomycosis. The composition includes Rose Bengal dye as a photosensitizer, which generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) when exposed to light, killing microbes. The enamel also contains polymers like cellulose acetate and PMMA to form a durable, water-resistant film, and lactic acid to enhance penetration. This formulation offers a convenient and effective way to treat nail infections with prolonged antimicrobial action.
- Psoriasis affects over 100 million people worldwide. Majority (75-80%) experience mild to moderate symptoms impacting quality of life and increasing depression risk.
- Treatments include topical agents and systemic therapies like methotrexate and biologics but face challenges penetrating thickened psoriatic epidermis, leading to reduced efficacy.
- Systemic therapies pose risks such as liver damage and carcinogenicity.
- Development of effective topical formulations is critical to overcome skin barrier challenges and improve treatment outcomes while minimizing side effects.
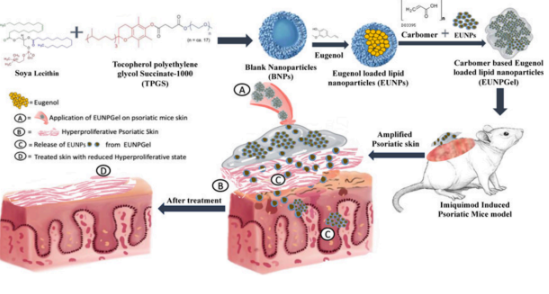
- Particle Size and Stability: EUNPL had a particle size of 205.6±2 nm, PDI of 0.23, and zeta potential of -27.08±0.9, ensuring colloidal stability.
- Imaging Confirmation: TEM and SEM confirmed particle size; SEM showed EUNPGel particle aggregation aiding skin adherence and efficacy.
- Encapsulation and Loading: Encapsulation efficiency was 85.7±2.3%, and loading capacity was 30.58±1.2%.
- Drug Release: Using the dialysis bag method, EUNPGel showed sustained drug release over 48 hours with 98.96±2.67% cumulative release, unlike the burst release in EUNPL and free eugenol.
- Sustained Release Mechanism: Sustained release in EUNPGel attributed to EUNPL embedding in carbomer gel, preventing burst release.
The prototype has been tested on:
- Microbial Cultures: EUNPL and EUNPGel were tested against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.
Wound Healing Model: In vivo testing on diabetic rat excision wound models.
It has shown the results as written in salient features.
- Improved Quality of Life: Effective treatment of psoriasis and related skin conditions can significantly enhance patients' quality of life by reducing symptoms such as itching, scaling, and discomfort, leading to better physical and mental well-being.
- Increased Accessibility: Versatile and stable formulations that are easy to apply and require less frequent dosing can improve accessibility to effective treatments, especially for those with busy lifestyles or limited access to healthcare facilities.
- Economic Benefits: Reduced frequency of application and enhanced treatment efficacy can lower overall healthcare costs by decreasing the need for additional medications, treatments, and doctor visits, benefiting both patients and healthcare systems.