The invention discloses a single-step, acid-free method for synthesizing reduced graphene oxide-like material (rGOL) from graphite using a water-based medium. The process involves dispersing graphite in an aqueous solution containing sodium nitrate and oxidizing it with potassium permanganate under mild conditions. This method avoids the use of concentrated mineral acids and toxic reducing agents. The resulting rGOL exhibits high electrical conductivity, reduced structural defects, and good dispersion stability. The material is produced on a gram scale and is suitable for applications requiring conductive, few-layer graphene-like nanostructures.
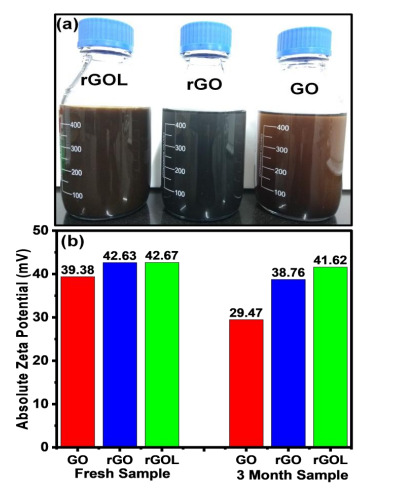
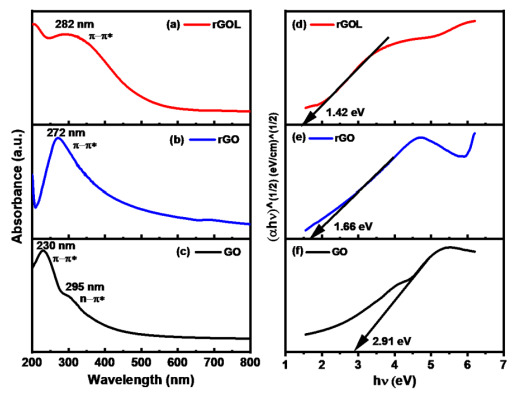
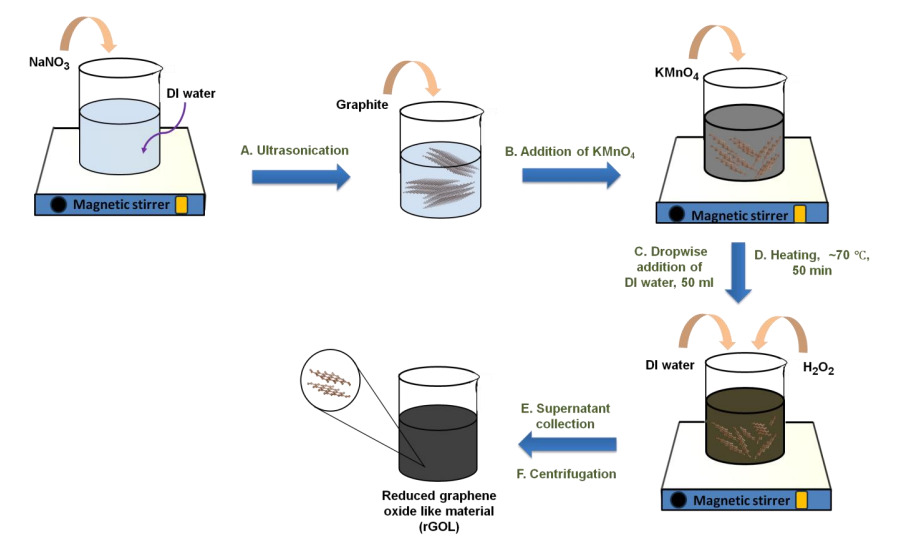
Figure (1a) Digital photograph of rGO like material, rGO (standard reduction method), and GO (modified Hummers method), (1b) zeta potential values for the fresh samples and after 3 months of storage time-duration. The rGO like material shows a good dispersion behaviour, similar to GO in water and exhibits long-term stability than rGO and GO. (2) UV-Visible spectra (2a - 2c) and their corresponding Tauc plots (2d - 2f) for the rGOL, rGO, and GO samples, respectively. The as-synthesized rGOL has a lower band gap (1.42 eV) than the rGO (1.66 eV). The GO has an optical band gap of 2.91 eV. (3) Schematic step-by-step view of the process for the exfoliation of rGOL material. NaNO3 aqueous solution is prepared under constant magnetic stirring: step A – addition of graphite under ultrasonication, step B – addition of KMnO4, step C – addition of DI water, step D ˗ providing some heat of 70°C, step E – supernatant collection, step F – centrifugation.
Conventional methods for producing reduced graphene oxide involve concentrated acids, hazardous chemicals, and multistep reduction processes that result in low electrical conductivity, structural defects, and environmental hazards. These methods also require long processing times, high temperatures, and complex purification, making them inefficient and unsustainable. There is a critical need for a safe, acid-less, single-step process to synthesize graphene-like materials from graphite with high yield, electrical conductivity, and reduced defects under ambient conditions.
- Acid-Free Synthesis Route: The method eliminates the use of concentrated acids and instead employs water, sodium nitrate, and potassium permanganate, making the process safer and more environmentally friendly.
- High Electrical Conductivity: The synthesized graphene-like product achieves a conductivity of 9.22 S/cm, which is significantly higher than that of conventionally reduced graphene oxide.
- Low Defect Density: A Raman ID/IG ratio of 0.80 confirms fewer structural defects and improved preservation of the graphenic lattice.
- Gram-Scale Yield and Mild Conditions: The process consistently yields approximately 77% of product within 2 to 3 hours at room temperature, demonstrating both scalability and efficiency.
- Nano-Sheet Morphology: The resulting graphene-like material forms few-layer nanosheets with thicknesses ranging from 1.5 to 3.6 nm, ensuring uniform dispersion and high surface area.
The prototype was developed at laboratory scale using standard lab equipment such as magnetic stirrers, centrifuges, and sonicators. Graphite powder was dispersed in deionized water containing sodium nitrate, followed by mild oxidation using potassium permanganate under controlled temperature and stirring. The reaction mixture was processed to isolate the product through filtration, washing, and drying steps. The reduced graphene oxide-like material (rGOL) was produced in gram-scale quantities and characterized using techniques such as Raman spectroscopy, FTIR, XRD, AFM, TEM, and electrical conductivity measurements. The prototype demonstrated reproducibility, high yield, and superior structural and electrical properties without the use of concentrated acids or toxic reductants.
The technology has been successfully demonstrated at laboratory scale, achieving gram-scale synthesis of reduced graphene oxide-like material with reproducible results. The process has been validated through comprehensive physicochemical characterization, confirming high conductivity, reduced defect levels, and structural integrity. The method is ready for pilot-scale translation and further scale-up for industrial applications.
4
This technology eliminates the use of hazardous concentrated acids and toxic reducing agents in graphene oxide synthesis, thereby reducing chemical waste, health hazards, and environmental pollution. Its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and use of water-based reagents make it highly suitable for safe adoption in academic, industrial, and decentralized setups. By enabling eco-friendly and scalable production of conductive graphene-like material, the invention supports sustainable manufacturing practices and advances the accessibility of nanomaterials for clean energy, electronics, and environmental applications.
- Flexible Electronics: Suitable for conductive films in flexible electronic devices
- Energy Storage Devices: Applicable in supercapacitors and battery electrodes due to high conductivity
- Printed Electronics: Useful in ink formulations for printed circuit applications
- Composites and Coatings: Enhances strength and conductivity in polymer nanocomposites
- Environmental Remediation: Can be used in adsorption-based filtration systems
- Sensors and Biosensors: Functions as an active material for chemical and biological sensing platforms
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202421000994
553462