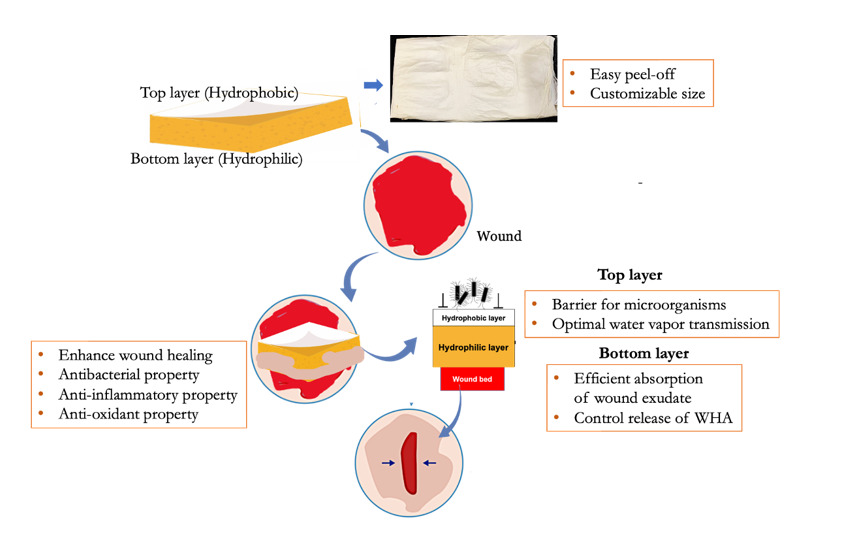
The invention relates to a bilayer dermal patch comprising a hydrophobic top layer and a hydrophilic porous bottom layer for wound dressing applications. The top layer forms a barrier against external contaminants while retaining moisture, and the bottom layer absorbs wound exudates and delivers therapeutic agents. The patch may incorporate wound-healing additives such as curcumin nanoparticles and soluble eggshell membrane (SESM) protein to provide antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects. Methods of preparation include solvent casting and electrospinning techniques, resulting in biocompatible and biodegradable wound dressings suitable for various acute and chronic wound types.
Conventional wound dressings such as gauze or cotton do not provide the necessary moist environment or therapeutic benefits essential for effective healing, especially in chronic wounds like burn, diabetic foot ulcers or pressure sores. These materials lack antimicrobial properties, do not facilitate cellular activity, and often require frequent replacement. Therefore, there is a need for a biocompatible, biodegradable, and multifunctional wound dressing that promotes rapid healing, prevents infection, and supports tissue regeneration through structural and therapeutic integration.
- Bilayer Patch Design: The dermal patch consists of a hydrophobic top layer and a hydrophilic porous bottom layer that together simulate the extracellular matrix (ECM) to support optimal wound healing. The top layer is composed of polycaprolactone (PCL) and chitosan, while the bottom layer uses polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), with the capability to embed curcumin nanoparticles and soluble eggshell membrane (SESM) protein for therapeutic benefit.
- Multifunctional properties: The polymer composition, nanoparticle concentration, and bilayer design provide multifunctional properties such as antibacterial and anti- inflammatory effects, support for fibroblast migration to the wound site, and moisture retention.
- Scalable and Customizable Fabrication: The patch can be manufactured using solvent casting or electrospinning methods, allowing control over thickness, porosity, and mechanical strength to suit various wound care applications.
Two types of dermal patch prototypes were developed: film-based and nanofiber-based. The film patch was fabricated by first forming a PCL-chitosan top layer through solvent casting, followed by the addition of a PVA-based bottom layer containing curcumin nanoparticles and soluble eggshell membrane (SESM) protein. The bilayer was crosslinked using glutaraldehyde vapors. The nanofiber version was prepared via electrospinning, where PCL-chitosan and PVA solutions were electro spun sequentially to form distinct layers. Both prototypes were tested for antibacterial activity, hemocompatibility, and wound healing efficacy using rat models, demonstrating enhanced performance compared to commercial wound dressings. Among both forms of the dermal patch, the electrospun fibrous product demonstrated superior wound healing ability. It is highly flexible and can be manufactured at large scale with low cost. A detailed preclinical study was conducted using a full-thickness excision model in rabbits, which showed promising results when compared to commercially available products.
Prototypes of the dermal patch have been successfully developed in both film and nanofiber forms using solvent casting and electrospinning methods. The patches have been characterized for structural, biological, and mechanical properties. In vitro antibacterial and hemocompatibility tests, along with in vivo wound healing studies on rat models, have demonstrated enhanced healing, biocompatibility, and therapeutic efficacy compared to commercial wound dressings. The technology has been validated at the lab scale, and preclinical assessments in rabbits are ongoing.
4
The dermal patch provides an affordable, multi-functional healing properties, and biocompatible wound care solution suitable for treating acute and chronic wounds, including full thickness, burn and diabetic foot ulcers. Its ability to promote faster healing, reduce infection risk, and minimize dressing changes can significantly improve patient outcomes, especially in resource-limited or rural healthcare settings. By using naturally derived and non-toxic materials, the technology also reduces environmental burden and enhances accessibility to advanced wound care.
- Chronic wound management including diabetic foot ulcers and pressure sores requiring enhanced healing and infection control.
- Post-surgical dressing materials where biocompatibility and moisture retention are essential for recovery.
- Burn treatment and skin injury care, utilizing antioxidant and anti-inflammatory components to promote tissue regeneration.
- Advanced wound care product development in the pharmaceutical and biomedical device industries.
- Rural and resource-limited healthcare systems needing affordable, effective, and easy-to-use wound dressing solutions.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202121018106
566964