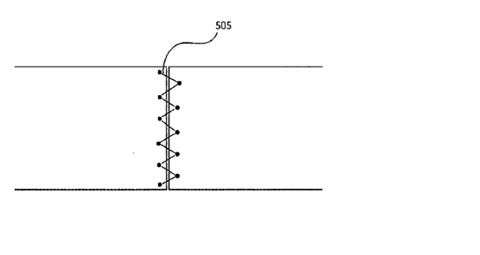
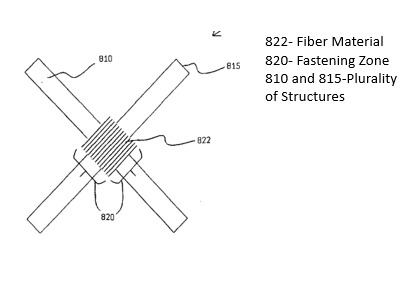
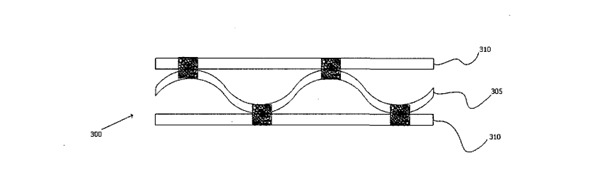
A method to join several structures together involves placing them in a fastening area and using a fiber material and resin to hold them in place. This forms a fiber material that soaks up the resin. The fastening area covers different parts of each structure. Then, the fiber material with resin is hardened (cured) to create a strong, durable bond between the structures.
Figure (1) Two dissimilar material plates joined together by impregnated fibre material in butt joint format, depicting a plurality of structures held by an impregnated fiber material; (2) Depicting a plurality of structures held by an impregnated fiber material; (3) Depicting a plurality of structures (different geometric configurations of materials like tubes) held together by impregnated fiber material creating a strong structure
Conventional methods of fastening metallic and non-metallic structures, such as mechanical fastening, welding, and bonding, tend to fail over time due to stresses, vibrations, and corrosion, particularly in environments such as vehicles where materials like aluminum are used. The existing methods have limitations, especially when joining materials that are difficult to weld or bond, such as aluminum. This invention addresses the need for a more durable, corrosion-resistant, and lightweight fastening solution.
- Durable Joints: The technology uses fiber materials impregnated with resin, leading to a durable, rigid, and long-lasting joint.
- Corrosion Resistance: The use of resin significantly reduces the risk of corrosion in the joints, especially when compared to traditional mechanical or welding methods.
- Reduced Mass: The method results in lighter joints, which is particularly advantageous in industries like automotive and aerospace where weight reduction is crucial.
- Versatility: The technology is applicable to both metallic and non-metallic structures, and can be used for various joint types, such as lap joints, butt joints, and complex multi-structure configurations.
- High Strength: The strength of the joint depends on the number of fiber layers used, providing customizable strength according to specific requirements.
- Cost-effective and Environmentally Friendly: The method avoids the need for energy-intensive processes like welding, making it more energy-efficient and cost-effective in certain applications.
- Easy to Implement: The use of fiber and resin is a relatively simple method that can be applied without specialized tools or equipment, making it accessible for a wide range of industries.
The prototype likely demonstrates the fastening of various structures using fiber material and resin. This includes holding the structures at a fastening zone, applying the resin-impregnated fiber material, and curing it to create a durable joint. While specific prototype models aren't detailed in the provided text, the technology can be tested using different materials and joint types, such as linear structures (pipes, cylinders) or planar structures (lap joints, butt joints).
The technology is at the stage of concept development.
2
The technology improves the longevity and safety of structural joints in infrastructure and construction, such as buildings, bridges, and vehicles. By reducing reliance on metal fasteners and lightening vehicle weight, it contributes to more fuel-efficient transportation, reducing the environmental footprint. The enhanced durability and corrosion resistance strengthen structural integrity, minimizing maintenance and increasing safety. Additionally, the method provides cost savings by lowering material expenses and reducing maintenance costs, making it an efficient and sustainable solution for various industries.
- Automotive Industry: Especially for joining aluminum or lightweight metal structures in vehicles
- Aerospace: Lightweight, high-strength joints are crucial in aerospace applications for reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity
- Construction and Infrastructure: Can be used in civil engineering for joining materials such as steel, concrete, and composite materials
- Marine Industry: Can be used in shipbuilding for joining metal and composite materials in marine environments prone to corrosion
- Renewable Energy: In solar panel and wind turbine structures, where durable and lightweight joints are essential for performance and longevity
- Manufacturing: General industrial applications where efficient, strong, and lightweight joints are needed.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
2880/MUM/2013
372969