This innovation is a method and system for assigning one or more mobile relays to source-destination pairs and intermediate stops in millimeter wave (mmWave) networks, achieving high data rates between sources and destinations. The method involves computing channel gains and data rates, and iteratively assigning relays, if required, to optimize network performance. This adaptive assignment ensures efficient use of mobile relays, mitigating blockage and propagation losses, and improving overall network reliability.
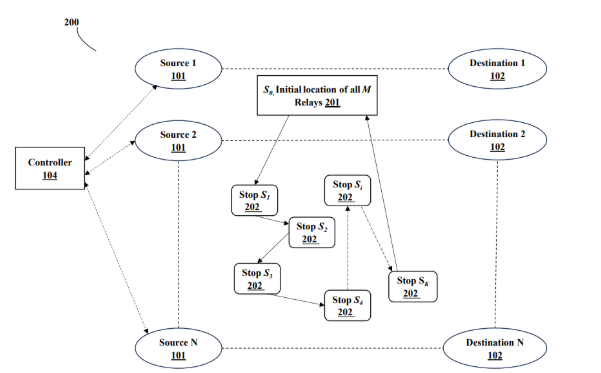
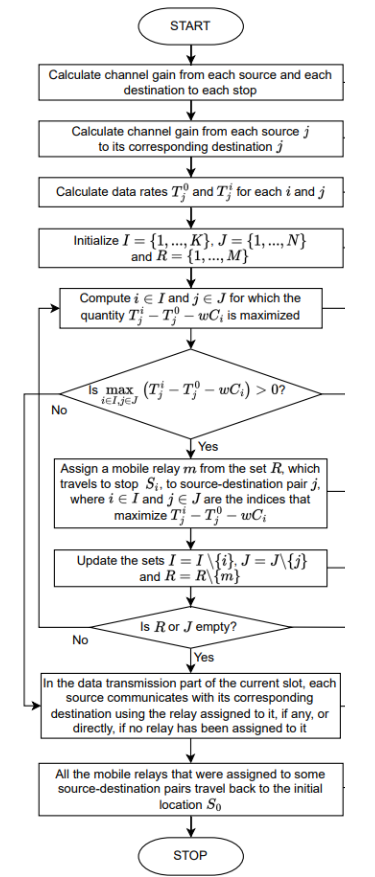
Figure (1) An example system, wherein the system comprises one 20 or more source-destination pairs, one or more mobile relays at initial location S0, a controller, and one or more intermediate stops, and the plurality of source-destination pairs and the plurality of mobile relays operate at mmWave frequencies; (2) Flowchart of the proposed method for the assignment of mobile relays to source-destination pairs and intermediate stops
Mobile relays are increasingly used in millimeter wave (mmWave) networks to mitigate blockage and propagation losses, enhancing network performance. However, the assignment of mobile relays to source-destination pairs and intermediate stops in each time slot remains a complex task, requiring careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance. This invention address these issues by providing a method for assigning one or more mobile relays to source-destination pairs and intermediate stops, optimizing data rates and network performance in mmWave networks.
- Adaptive Relay Assignment: This invention provides an iterative method to assign mobile relays to source-destination pairs and intermediate stops, optimizing data rates and network performance.
- Channel Gain and Data Rate Calculation: It employs channel gains and data rates to assess the best potential for communication.
- Iterative Optimization: This method uses an objective function to determine the optimal assignment of relays, taking into account energy costs for moving the mobile relays and data transmission rates.
- Minimization of Blockage and Propagation Losses: It ensures that the assignment of relays minimizes blockage and propagation losses, enhancing network reliability.
The prototype consists of a mmWave network with sources, destinations, intermediate stops, mobile relays, and a central controller. The network operates at mmWave frequencies, and the assignment process is modeled using a centralized controller that computes channel gains, data rates, and relay assignments iteratively. The system includes a controller that simulates the channel measurement, relay assignment, and data transmission phases.
Testing and evaluation of basic concept is under process for the final objective.
3
This technology enhances the efficiency and reliability of mmWave communication networks, which are critical for 5G and beyond 5G wireless networks. By optimizing the use of mobile relays, it can significantly improve data rates, reduce delays, and enhance the overall user experience. This is particularly beneficial for applications such as autonomous vehicles, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and large-scale data processing tasks, leading to more efficient and effective communication infrastructure.
- Wireless Networks: Enhances mmWave network performance and reliability
- Autonomous Vehicles: Improves communication between vehicles and infrastructure
- Internet of Things (IoT): Supports real-time data transmission in IoT devices
- Telecommunications: Enables high-speed data transmission in 5G networks
- Data Centers: Optimizes data transmission in high-performance computing environments
- Smart Cities: Provides robust communication infrastructure in urban environments
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202321089373
561073