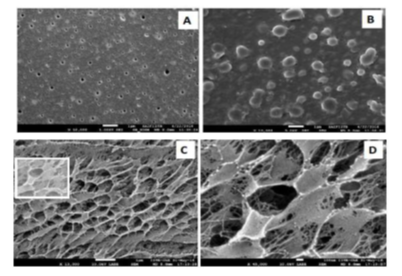
This invention introduces an eco-friendly method to create metal nanoparticles embedded in a polymer using natural sunlight. The process involves mixing a polymer solution with a natural reducing agent and metal salts, then exposing the mixture to sunlight for a few minutes. This green synthesis method uses bio-reducing agents and sunlight to facilitate the in-situ formation of metal nanoparticles within a polymer matrix, achieving uniform, spherical particles with diameters ranging from 10 to 50 nm.
Current methods of synthesizing metal nanoparticles embedded in polymers rely on chemical processes that are environmentally harmful. This invention addresses the need for a greener and more efficient synthesis approach by utilizing bio-reducing agents and sunlight to produce uniform metal nanoparticles within a polymer matrix.
- Eco-friendly Method: This technology uses eco-friendly method using sunlight and bio-reducing agents for nanoparticle synthesis.
- Polymer Mixing: It follows a simple process involving polymer solution mixing and sunlight exposure for rapid results.
- Versatile Polymer Options: It uses customizable polymer options to enhance versatility for various applications.
- Plant-based Agents: Natural bio-reducing agents ensure biocompatibility and environmental friendliness. It uses green chemistry method, which utilizes plant-based bio-reducing agents.
- Uniform Spherical Nanoparticles: This produces uniform spherical nanoparticles with diameters of 10-50 nm are produced. This is a sunlight-driven synthesis that enables rapid nanoparticle production. It results in uniform spherical nanoparticles with consistent size.
The method successfully synthesizes polymer-embedded metal nanoparticles, specifically silver, using bio-reducing agents and sunlight exposure within 5 minutes.
The in situ formed nanoparticles are spherical, with diameters ranging from 10 to 50 nanometers, and exhibit antimicrobial properties.
The technology leverages green synthesis, reducing the need for toxic chemicals, and has shown effective and rapid nanoparticle formation.
This technology advances drug delivery and diagnostic technologies enhancing patient care and treatment outcomes. Green synthesis methods used in the process reduce environmental impact, promoting sustainable practices in nanoparticle production.
- Biomedical Innovations: Enable advanced drug delivery and imaging technologies
- Environmental Solutions: Aid in water purification and pollution control efforts
- Enhanced Food Safety: Improve packaging materials with antimicrobial properties
- Energy Advancements: Drive innovation in solar cells and sensors with efficient nanoparticle integration
- Other Relevant Industries: Healthcare, sustainable development, manufacturing industries
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202121046488
405579