This invention presents a novel design for surpassing the diffraction limit in optical imaging systems. The Q-shaped plasmonic resonant aperture (QPRA) utilizes surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) to achieve sub-wavelength focusing, providing enhanced resolution essential for applications in nano-optics, biology, and nanolithography.
Traditional lenses are limited by the diffraction limit, restricting the tightness of light confinement. This limitation prevents advancements in various high-precision fields, necessitating a solution that can achieve super-resolution beyond this physical barrier.
- This innovation breaks the diffraction limit to achieve super-resolution.
- It enables tight focusing of linearly polarized light without split focal spots.
- Simple generation of linearly polarized light is possible for diverse applications.
- It offers cost-effective high-resolution imaging without the need for ultraviolet wavelengths.
- It has compact optical components suitable for high-density integration.
- It utilizes Surface Plasmon Polaritons (SPPs) for extreme confinement of electromagnetic fields.
- It features a Q-shaped Plasmonic Resonant Aperture (QPRA) with a nano-antenna tip for single-spot super-focusing.
- Its sub-wavelength slits compensate phase mismatches in SPPs.
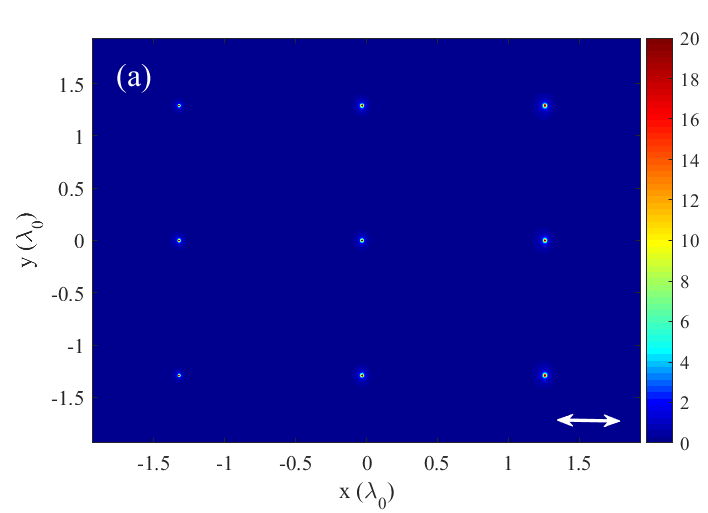
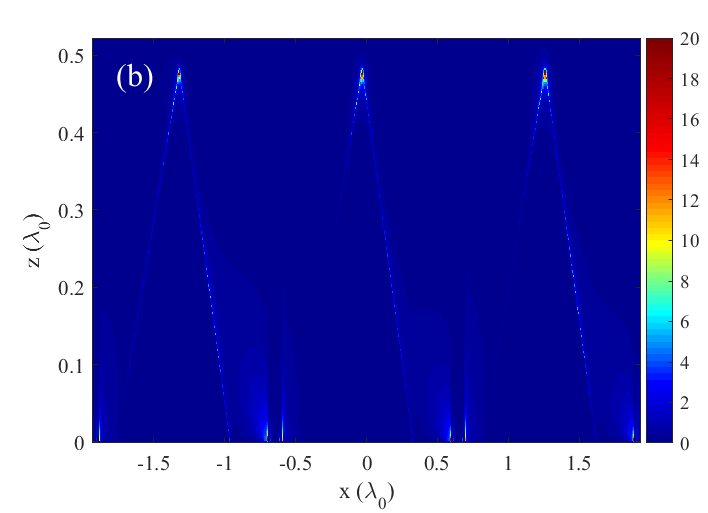
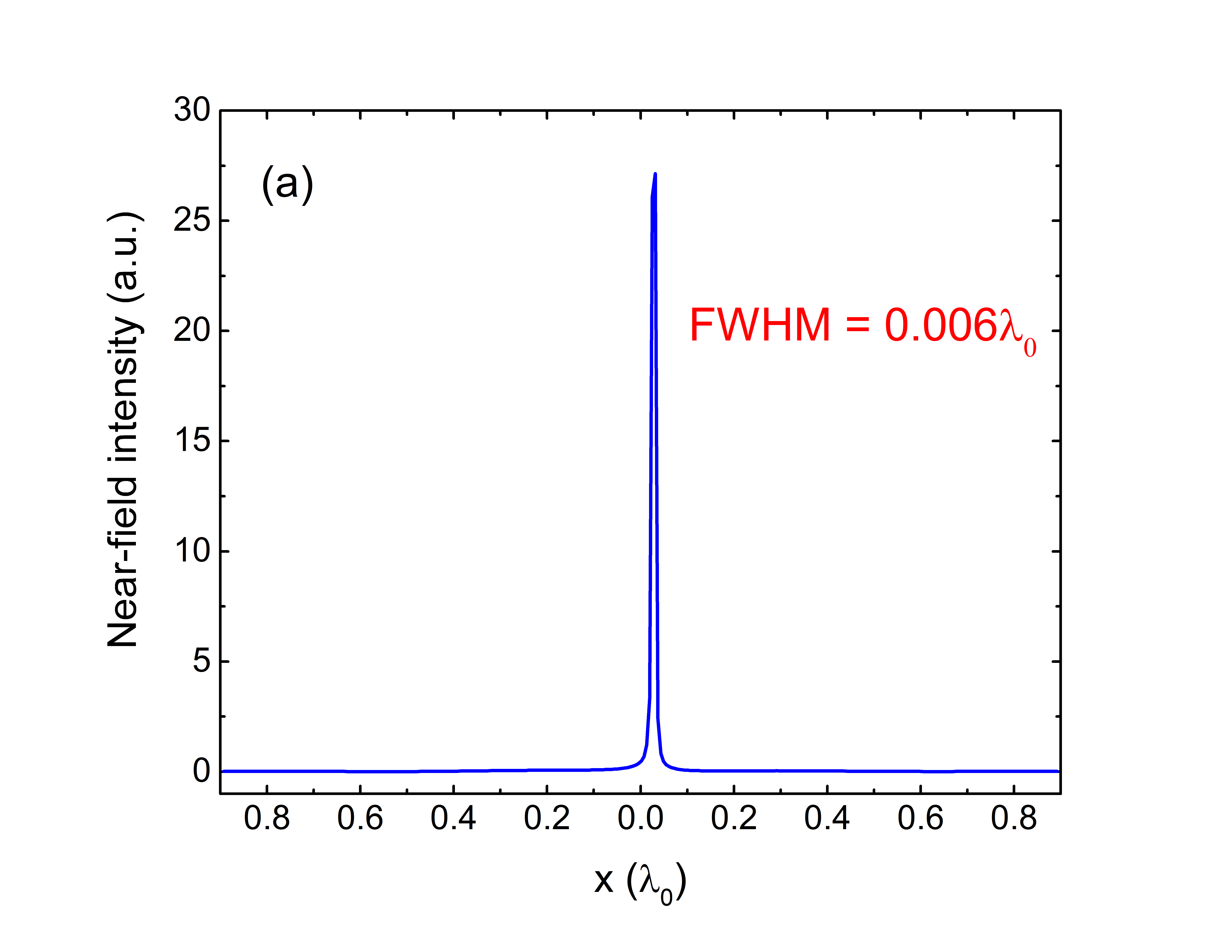
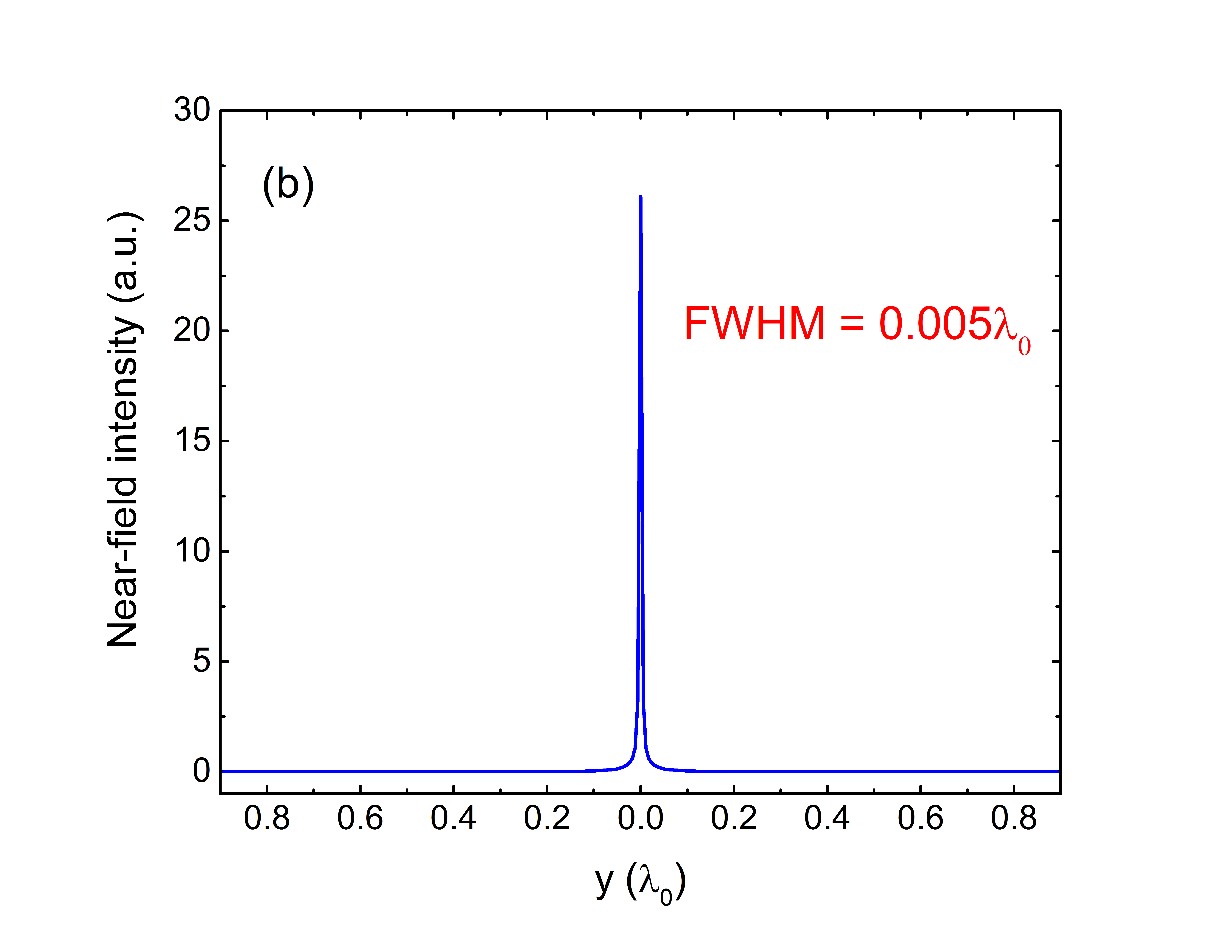
- Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) simulations confirm the efficiency of the design, with focusing of light to a region of λ0/168.
The prototype consists of a Q-shaped aperture milled in a plasmonic film with a nano-antenna tip placed at the center. The dimensions and geometry of the QPRA and the tip are optimized to achieve super-resolution focusing, as validated by SEM imaging and electric field intensity distribution analyses.
The QPRA has been fabricated and its focusing properties have been verified through simulations and experimental setups, demonstrating its ability to surpass traditional optical limits.
3
The technology offers significant advancements in medical diagnostics, efficient solar cells, and high-capacity optical information systems. By enabling higher resolution imaging at lower costs, it holds the potential to revolutionize fields requiring precise light manipulation and nano-fabrication.
- Nanotechnology - Nanolithography, Nanoimaging
- Tip Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (TERS)
- Near-field Scanning Optical Microscopy (NSOM)
- Medical imaging and diagnostics
- Semiconductor manufacturing
- Optical communication and data storage
- Solar energy
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202221055256
455379