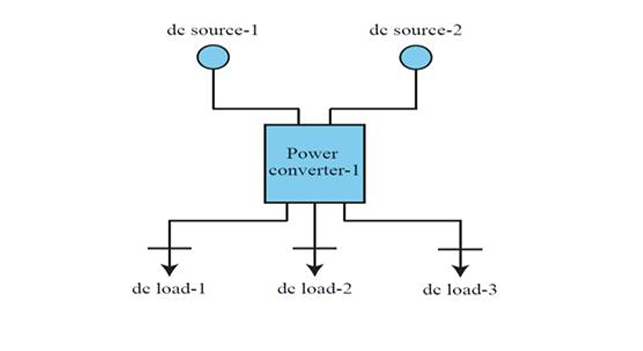
An on-board charging system combines two separate chargers into one compact unit. It uses a smart three-port converter to feed both the traction driving battery and the auxiliary battery. Various topological modifications for designs suit scooters, cars, and heavy vehicles, all aiming for lower cost and size.
Electric vehicles (EVs) usually need two separate chargers—one for the high voltage traction battery and another for the low voltage auxiliary battery that powers lights, dashboard, and other auxiliary loads. Using separate chargers increases cost, complexity, and space inside the vehicle. Current systems often is complex and cannot charge both batteries efficiently from utility grid.
- Smart Single-Unit Charging: Product charges both the main and auxiliary batteries at once, eliminating duplicate hardware.
- Flexible Multi-Port Converter: Topology adapts to different vehicle types, from two-wheelers to heavy trucks, by changing simple components.
- Compact and Energy-Saving: This feature reduces bulky transformers and extra switches, cutting weight, volume, and power losses.
- Easy Manufacturing with Off-the-Shelf Parts: This topology uses lesser switches, diodes, and inductors compared to existing topologies, keeping production costs low.
Working prototypes have been built using printed circuit boards and standard power-electronic components. Multiple converter layouts (fully active, semi-active, single inductor) have been assembled and tested on a bench with emulated batteries and grid input.
A detailed working design has been developed with several test variations for different types of EVs. The system has been studied for performance under real-world conditions such as temperature, voltage, and battery load.
6
By removing redundant parts and making charging more efficient, this system lowers both upfront and running costs, bringing electric vehicles into reach for more buyers. Less wasted energy eases strain on the power grid and makes it simpler to pair EV charging with solar or wind sources. A leaner charger design speeds up assembly and cuts service time, which reduces production and maintenance expenses. The current technologies are meant for onboard chargers and not for charging stations.
- Electric two-wheelers and three-wheelers: Compact single-unit chargers extend scooter and auto-rickshaw range while cutting cost and weight.
- Passenger electric cars and commercial EVs: Integrated onboard chargers streamline wiring and improve charging speed for cars, buses, and delivery fleets.
- EV component manufacturers: Modular multi-port converter designs simplify production and reduce inventory of separate charger parts.
- Automotive and green mobility sectors: Scalable charging technology supports large-scale deployment of eco-friendly vehicle fleets.
- Clean energy and sustainable transportation initiatives: Efficient battery charging aligns with renewable power use and lowers overall carbon footprint.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202221067778
565035