A system and method for obtaining Inelastic Tunneling Spectra (IETS) from Current(I)-Voltage(V) characteristics are disclosed. The method involves filtering the I-V data using a median filter, estimating noise levels, and applying Tikhonov Regularization to compute the first and second derivatives. The system includes an electronic controller, a Digital to Analog Converter (DAC), an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC), and a display unit. This approach eliminates the need for additional instrumentation, making it compact and cost-effective.
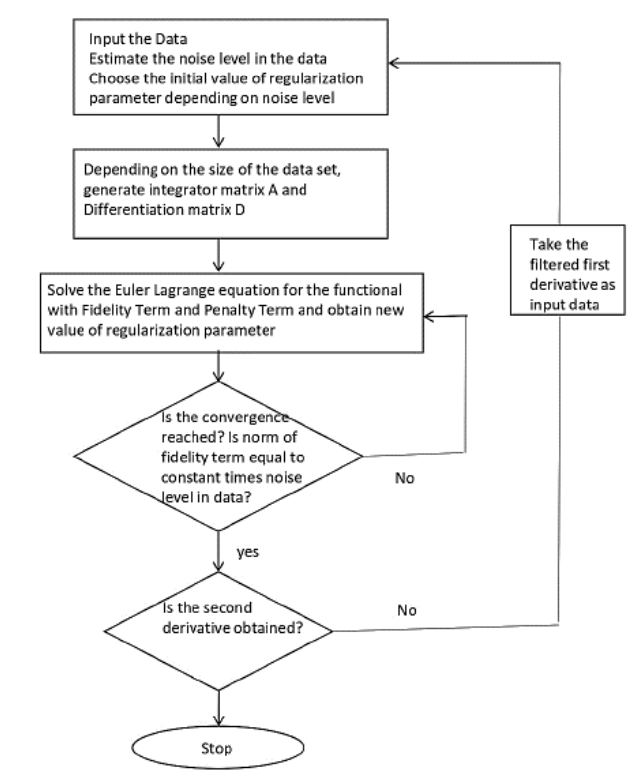
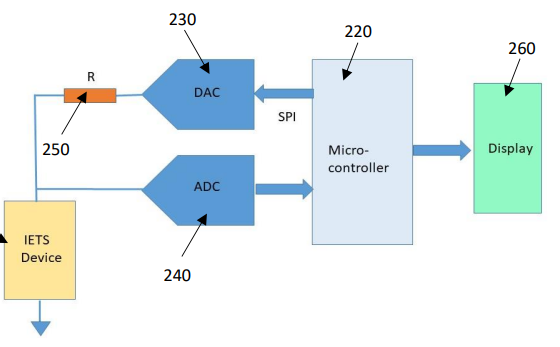
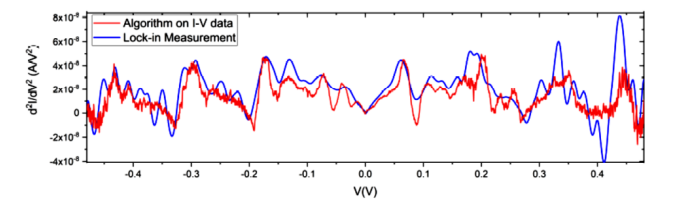
Figure (1) Flow chart of the method for obtaining noise-filtered second derivative of the Current(I)-Voltage(V) characteristics of an IETS device; (2) Schematic of the system for obtaining Current(I)-Voltage(V) characteristics of an IETS device; (3) Comparison of lock-in measurement second derivative and the second derivative of the I-V data from the filtering process
Conventional methods for obtaining Inelastic Tunneling Spectra (IETS) from Current(I)-Voltage(V) characteristics require additional instrumentation, making them bulky, expensive, and limited in application. Direct computation of derivatives from noisy I-V data is unreliable due to the amplification of noise. There is a need for a compact, cost-effective method and system that can filter noise while calculating derivatives to obtain IETS without additional instrumentation.
- Noise Filtering: The method uses a median filter to estimate noise levels and Tikhonov Regularization to compute derivatives, effectively reducing noise.
- Compact Design: The system does not require additional instrumentation, making it compact and cost-effective.
- High Sensitivity: The method accurately computes IETS peaks from I-V data, matching lock-in measurements.
- Fast Computation: The I-V measurement and derivative computation are fast, reducing overall detection time.
- Versatile Applications: The system is suitable for various applications, including food, agriculture, security, clinical diagnosis, and environmental monitoring.
The prototype consists of an electronic controller (e.g., STM 32 series microcontroller or Raspberry Pi board) connected to an IETS device through a Digital to Analog Converter (DAC) and an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC). A resistor is used to measure the current through the IETS device. The system is configured to apply a ramp voltage to the IETS device, measure the voltage across it, and compute the first and second derivatives of the I-V data using Tikhonov Regularization. The results are displayed on a connected display unit.
Basic formulation confirmation; stage of realistic representation of end use
4
This invention enables the development of compact and cost-effective IETS-based sensor systems, which can be widely deployed in various applications such as food safety, environmental monitoring, and clinical diagnosis. The reduced need for additional instrumentation makes it more accessible and practical for field use. The high sensitivity and fast computation capabilities of the system enhance its reliability and efficiency in detecting molecular fingerprints, contributing to advancements in biomimetic electronic nose technology, or to IETS-based physico-chemical analysis.
- Food Safety: Detecting contaminants and spoilage in food products
- Agriculture: Monitoring soil and crop health
- Security: Identifying hazardous substances in real-time
- Clinical Diagnosis: Detecting biomarkers for disease diagnosis
- Environmental Monitoring: Monitoring air and water quality
- Research and Development: Studying molecular interactions and properties
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202021034422
563360