This method describes a solvent casting method for fabricating high strength material using High Density Polyethylene (HDPE). It involves preparing an HDPE solution suitable for composite manufacturing through a series of steps. Initially, HDPE pellets are processed into filaments using a twin extruder and subsequently chopped into small pieces of approximately 1 mm size using a chopper machine. The HDPE powder is then combined with xylene in specific proportions and stirred at 900–1100 rpm (110°C–140°C) for 1–3 hours to form a homogeneous solution. The resulting HDPE-xylene solution is poured into a petri dish and allowed to cool naturally at ambient temperature for 10–20 minutes, resulting in the formation of solvent-casted HDPE material.
Conventional methods for manufacturing High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), such as injection molding and extrusion, require high capital investment, complex machinery, and significant energy, making them unsuitable for cost-effective, small-scale production. Existing solvent casting methods used for other polymers are often incompatible with HDPE due to its high melting point and chemical resistance, requiring additional steps like quenching or solvent extraction. Thus, a simplified, efficient, and cost- effective solvent casting process is needed to fabricate high-strength HDPE materials with uniform properties and minimal post-processing.
- Solvent Casting for HDPE: A novel application of the solvent casting technique to fabricate high-strength HDPE materials, which is traditionally challenging due to HDPE's high melting point and chemical resistance.
- Low-Cost and Scalable Process: It eliminates the need for complex machinery like injection molders, significantly reducing capital and operational costs.
- Optimized Parameters: Defined parameters for solvent ratio (1:3 HDPE: xylene), stirring speed (1000–1100 rpm), and temperature (110°C–140°C) ensure homogeneity and reproducibility.
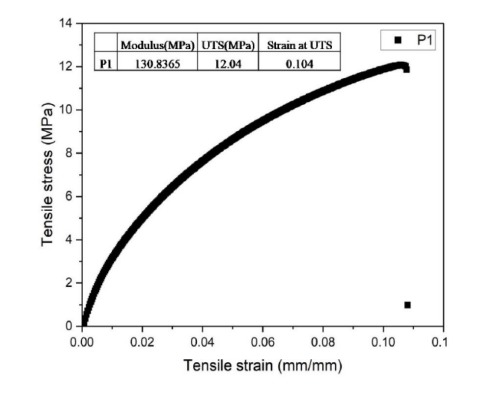
- Enhanced Mechanical Properties: The solvent-casted HDPE shows a tensile strength of 12 MPa and a modulus of 130 MPa, suitable for structural and functional applications.
- Environmentally Conscious: It promotes the reuse of HDPE waste, supporting sustainable practices and circular economy principles.
- Accessible Fabrication Method: The simplified process is adaptable for small- scale production and academic research, making it viable for decentralized or rural manufacturing setups.
NA
5
The technology offers a low-cost, energy-efficient alternative to conventional HDPE processing, making it accessible to small industries and educational institutions. It promotes reuse of HDPE waste, aiding sustainability and reducing environmental impact. The simplified method minimizes machinery needs, supports localized manufacturing, and provides an accessible platform for research and hands-on learning in material science.
- Packaging and consumer goods manufacturing
- Water treatment and membrane technologies
- Academic and industrial research in polymer science
- Medical and pharmaceutical packaging
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202421012245
559586