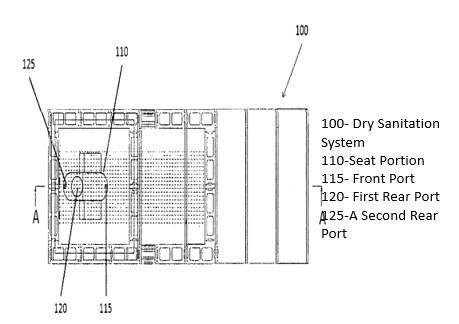
The present invention is a dry sanitation system which comprises of a squat type seat portion comprising a front port for collecting urine, a first rear port and a second rear port for collecting solids and washing water respectively. A separator below the seat portion to separate solid and washing water into solid pit and washing water pit respectively and a urine pit to collect urine and a compositing space to carry out aerobic decomposition of the solid waste. The pits can be totally underground, partially underground or totally above the ground, with provision of access to empty the pits whenever required. The dry sanitation system is also useful to dispose disposable sanitary pads and disposable diapers. This system has foot rest with inclination to support heel of the users especially elderly person and making the squatting position comfortable.
Conventional sanitation systems are heavily reliant on water for flushing and maintaining water traps, which creates significant challenges in water-scarce regions. Additionally, traditional systems mix fecal matter, urine, and washing water, leading to the creation of blackwater that results in wastewater pollution. This mixing also wastes valuable nutrients found in human excreta that could be used as fertilizers. The need for a dry sanitation system that separates waste components for efficient decomposition and reuse has become essential.
- Separation of Waste Components: The system separates solids, urine, and washing water into distinct compartments, enabling independent processing of each component.
- Aerobic Decomposition: Solids are allowed to decompose aerobically without the use of chemicals, enzymes, or bio enzymes, making the process environmentally friendly.
- Urine Preservation: The system ensures that nitrogen-rich urine is preserved by preventing oxidation, retaining its value as a fertilizer.
- Hygiene Improvement: The separation of waste reduces foul odor and pathogen spread, improving the overall hygiene of the system.
- Sustainability: The system promotes the reuse of human waste as organic fertilizer, reducing reliance on industrial fertilizers and promoting a sustainable nutrient cycle.
- Disposal of Sanitary Products: The system allows for the direct disposal of sanitary pads and diapers into the solids pit without clogging or negatively impacting the decomposition process.
The prototype consists of a seat portion with three distinct ports for urine, solids, and washing water. Below the seat portion, an inclined sieve separates solids from liquids, directing urine to a separate pit and washing water to a designated filtration area. The solids are directed into a composting space for aerobic decomposition. The system also includes a urine pit with an air shield to preserve nitrogen and prevent foul odors. Additionally, a self-closing flap mechanism prevents odors and insects from entering the toilet shelter.
System is ready to be deployed.
9
The dry sanitation system promotes water conservation by eliminating water-based flushing, making it ideal for water-scarce regions. It offers sustainable waste management by separating and aerobically decomposing waste into organic fertilizer, reducing the environmental impact of traditional methods. The system enhances health and hygiene by controlling odors and minimizing disease transmission, especially in rural areas. Additionally, it improves resource efficiency by using human excreta as fertilizer, reducing reliance on industrial fertilizers.
- Water-Sensitive Areas: The technology is particularly relevant in water-scarce regions where water conservation is critical.
- Agriculture: The technology can be used to produce organic fertilizer, enhancing soil fertility and reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers.
- Sustainability and Environmental Management: The system aligns with sustainability goals by reducing water usage, pollution, and promoting waste-to-resource technology.
- Public Health and Sanitation: The technology is useful in improving sanitation in rural, remote, and underdeveloped areas, contributing to better hygiene practices.
- Off-Grid and Remote Communities: It is ideal for locations without access to traditional sewage systems or where conventional sanitation solutions are not feasible.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
645/MUM/2014
498684