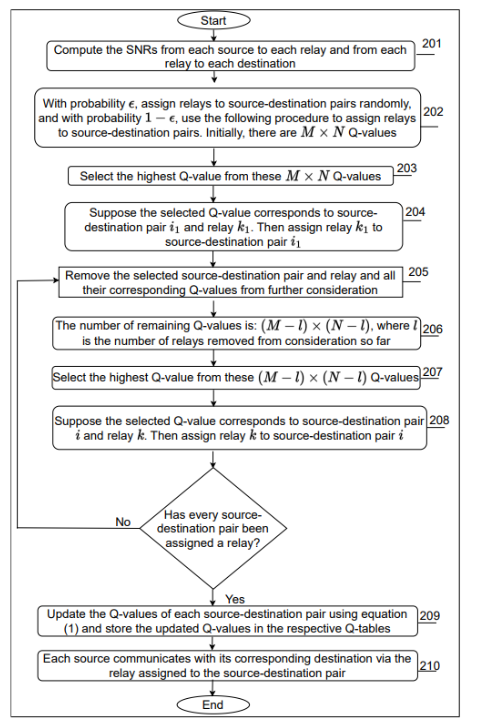
This invention provides systems and methods for relay selection in mmWave networks using a Q-learning based approach. The method optimizes throughput and reduces switching costs by dynamically selecting relays based on the highest Q-values. It supports both single and multiple source-destination pairs, ensuring efficient communication in each time slot. The Q-learning mechanism learns from past experiences to improve future relay selections, thereby enhancing network performance.
The increasing demand for network capacity and reduced latency in wireless networks, particularly in mmWave bands, necessitates efficient relay selection strategies to overcome high propagation loss and blockage issues. This invention addresses these limitations by proposing a Q-learning based relay selection method that optimizes throughput and reduces switching costs, thereby enhancing the efficiency and reliability of mmWave networks.
- Q-learning Based Relay Selection: The method uses Q-learning to dynamically select relays, optimizing throughput and reducing switching costs.
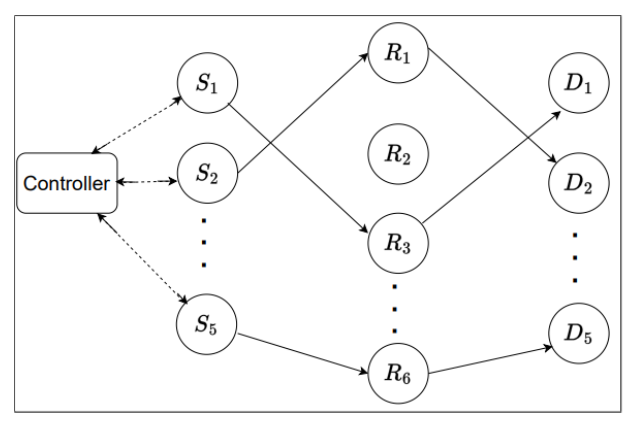
- Support for Multiple Source-Destination Pairs: The system can also be extended to assign relays to multiple source-destination pairs in each time slot, improving overall network efficiency.
- Dynamic Relay Assignment: The Q-learning algorithm updates Q-values based on past performance, ensuring optimal relay selection in real-time.
- Efficient Communication: The selected relays enable efficient communication between sources and destinations, reducing propagation loss and blockage issues.
The prototype consists of a mmWave network system comprising a source, a destination, and multiple relays. The system uses a controller to measure SNRs from the source to each relay and from each relay to the destination. The controller then selects a relay using the Q-learning algorithm, updates Q-values based on the received reward, and assigns the relay for communication. The prototype demonstrates the method's effectiveness in improving network throughput and reducing switching costs.
Testing and evaluation of basic concept for the final objective.
3
This technology significantly enhances the performance and efficiency of mmWave networks, which are crucial for 5G and beyond 5G communications. It supports the development of high-speed, low-latency wireless networks, benefiting industries such as telecommunications, IoT, and autonomous vehicles.
- Telecommunications: Enhancing network capacity and reducing latency in 5G and beyond 5G communications
- IoT: Improving data transmission in IoT networks, enabling more efficient and reliable communication
- Autonomous Vehicles: Supporting real-time communication and data exchange in autonomous vehicle networks
- Telemedicine: Facilitating high-speed, low-latency communication for remote medical services
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202321040358
551440