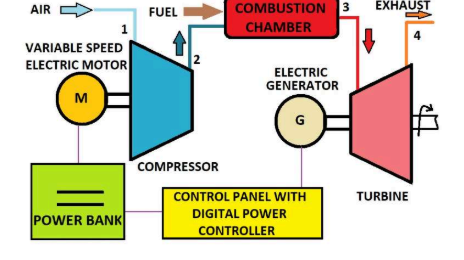
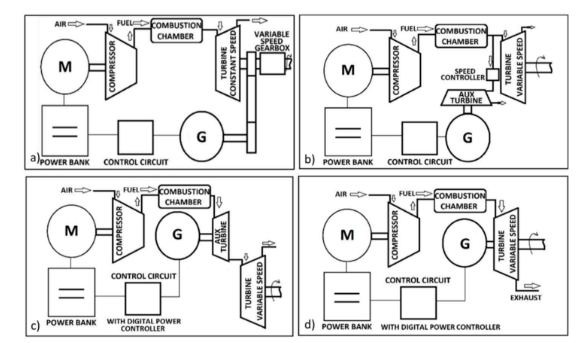
The Part Electric Gas Turbine (PEGT) is an innovative propulsion system designed to enhance the part-load efficiency, along with significantly lower design & development cost and time. By employing a variable-speed electric motor to drive the compressor, the PEGT allows independent operation of the compressor and turbine, addressing the challenge of iterative component matching and easing the design & development process. The open architecture configuration achieved by splitting the compressor and turbine shafts, provides flexibility, modularity, and maintainability of gas turbine components, while offering better off-design and part-load efficiency characteristics than conventional gas turbines. This configuration is expected to provide significant benefits in all propulsion and power generation applications in terms of improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions through better combustion techniques and simplification of control systems through simultaneous air and fuel control. The PEGT's flexibility in engine component architecture and ability to utilize compressors (including centrifugal types) further contributes to versatility in applications across multiple fields with superior overall performance and operational safety.
The Part Electric Gas Turbine (PEGT) addresses limitations of conventional gas turbines, which suffer from poor part-load efficiency, high specific fuel consumption, complex control systems, as well as an iterative and costly design and development process. By employing a variable-speed electric motor to drive the compressor, PEGT allows independent operation of the compressor and turbine, enhancing component-level and overall efficiency and performance. This innovation aims to optimize fuel use, reduce emissions, and simplify control mechanisms, particularly benefiting marine propulsion, automotive applications, and power generation.
- Independence of Components: The uniqueness of PEGT lies in its innovative split configuration, where a variable-speed electric motor drives the compressor independently from the turbine. This design decouples the compressor and turbine mechanically, allowing each component to function at its optimal efficiency. This configuration enhances part-load performance, reduces fuel consumption, simplifies the control system, and reduces design & development cost as well as time.
- Flexibility in Engine Component Architecture: Its flexible engine component architecture, allows use of multiple compressors, including centrifugal type, with more geometrical flexibility offering modularity, redundancy, maintainability, and significant improvement in overall gas turbine performance.
- Improved Efficiency: This innovation overcomes the poor part-load efficiency of conventional gas turbines by using a variable speed electric motor for the compressor.
- Simpler and Safer Control System: A simplified control system can be employed, with simultaneous air and fuel control, enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
- Smaller Intake Ducts: It is especially beneficial for marine applications, reducing intake losses and improving overall efficiency.
- Combustion Optimisation: It allows better combustor designs offering advanced combustion techniques like lean combustion, resulting in better fuel economy, multi-fuel capability, reduced emissions, and enhancing overall performance.
The PEGT prototype involves a split configuration with an electric motor-driven compressor, which provides compressed air to the combustor and a turbine generating mechanical power. The turbine is driven by high-energy combustion products from the combustor, which is fed with compressed air and fuel. The system includes a power generator to supply electricity to the compressor motor, ensuring continuous operation and improved efficiency.
Feasibility study has been done using numerical methods. Now, some industries are interested in building the prototype and a full-scale model.
3
The PEGT can significantly reduce design and development cost, improve fuel efficiency, especially at off-design or part-load conditions, and reduce emissions through optimized combustion techniques in applications such as marine propulsion and power generation. By offering better part-load efficiency, it contributes to more sustainable and economical operation of gas turbines, as well as their wider utility across multiple applications.
- Marine Propulsion: It offers significant advantages in efficiency (including off-design and part-load efficiency) and space utilization, reducing the size of intake ducts and enhancing overall performance.
- Automotive Propulsion: It potentially leverages uniqueness of electric drive within the engine configuration for hybrid electric propulsion, offering reduced weight, high endurance, and improved engine performance & fuel efficiency.
- Power Generation: It provides a more efficient and flexible alternative to conventional gas turbines, especially under variable load conditions.
- Aerospace Applications: It is a good fit for electric aerospace propulsion, with compact electric motor designs offering better endurance.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
201821023822
430837