This invention is about a new type of electric motor that is compact, energy-efficient, and easy to manufacture. Unlike regular motors that use heavy coils and metal parts, this design places flat coils directly on printed circuit boards (PCBs). These coils are arranged in a special wave pattern that helps the motor perform better while wasting less energy. The technology is designed to be used in electric vehicles, robots, and other smart machines where space and efficiency matter the most.
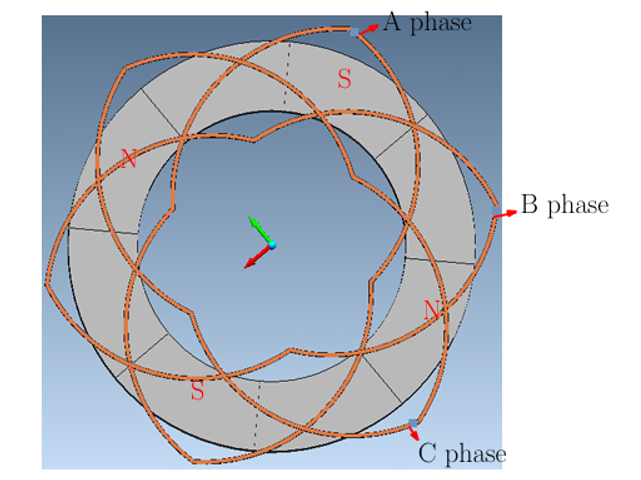
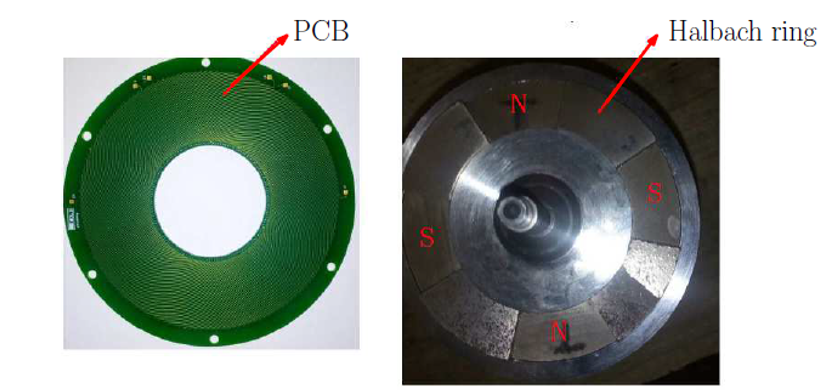
A coreless AFPM motor offers benefits like compact size, high power density, no reluctance torque, and low vibration. It also avoids axial pull between the stator and rotor and eliminates stator core loss at high speeds. However, challenges include managing leakage flux and reducing copper loss. Over the years, various coreless AFPM designs have been explored using different techniques to reduce flux leakage. With PCB technology advancements, stator windings can now be printed on circuit boards. This patent proposes a wave-type winding printed on the stator PCB, offering a simpler, more efficient, and reliable design for coreless AFPM motors.
- Compact PCB-Based Design: This technology replaces bulky motor coils with printed circuit board windings, making the motor lightweight and easy to integrate into small devices.
- Uniform Coil Arrangement: This product uses wave-type coil designs that are evenly spread, helping the motor generate more force with less energy and ensuring better performance.
- Reduced Energy Loss: This design ensures that all coil parts contribute to the motor’s rotation, reducing wasted energy and improving the overall efficiency of the motor.
- Multilayer Structure for Low Resistance: This technology reduces the resistance in the wires by distributing the coil across multiple PCB layers, which helps the motor run cooler and last longer.
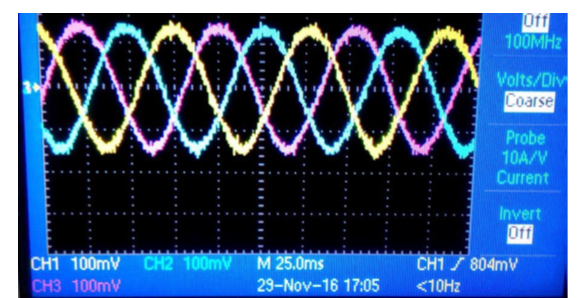
- Sinusoidal Output for Smooth Operation: This product generates smooth electrical signals that improve the motor's performance, especially in applications requiring precise and noise-free operation.
Detailed computer simulations and technical illustrations have been developed to demonstrate the working principles. These simulations confirm that the proposed design performs better than traditional motors in terms of efficiency and energy usage. A working prototype of a high-speed, low power 4-pole AFPM motor with PCB stator and Halbach rotor was built. Torque and efficiency were measured on a high-speed test setup up to 30000 rpm to verify performance gains over conventional designs.
The design has been developed and tested as a working prototype. Performance data like torque, magnetic efficiency, and cost savings have been compared with traditional motors.
5
This technology holds potential to significantly reduce the energy consumption of electric motors used in day-to-day devices like electric scooters, household appliances, and drones. With better efficiency, it supports the global push toward clean energy and helps reduce our carbon footprint. By making motors smaller and easier to produce, this invention can also lower the cost of energy-efficient products, making them accessible to more people. In rural or developing regions, such low-cost, low-maintenance motors can power essential tools and appliances, improving quality of life. Additionally, the reduced noise and heat emissions can contribute to safer, healthier urban environments.
- Electric vehicles
- Drones and UAVs
- Home appliances
- Industrial automation
- Consumer electronics
- Robotics
- Renewable energy systems
- Smart home technology
- Mobility devices for healthcare
Geography of IP
Type of IP
201721035017
498474