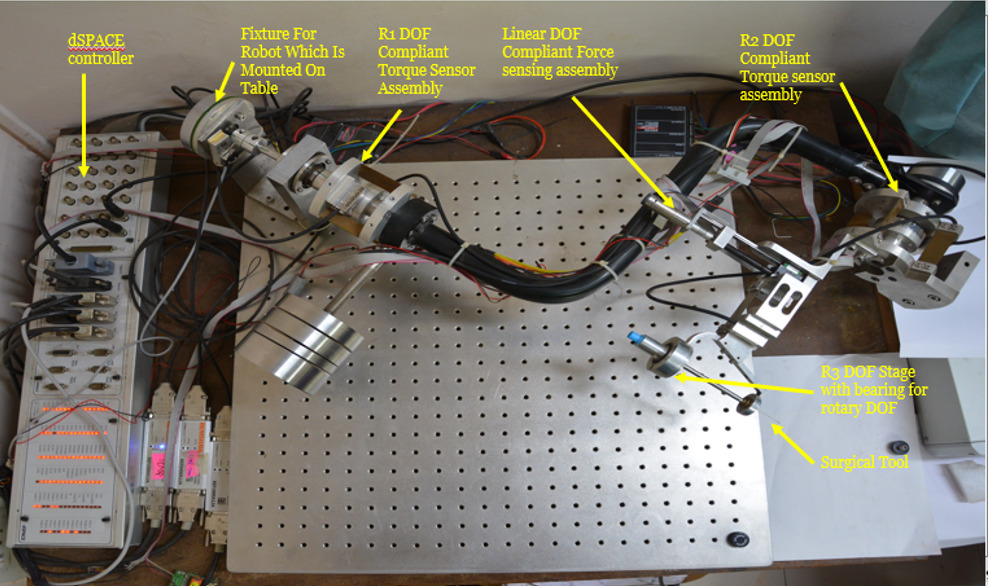
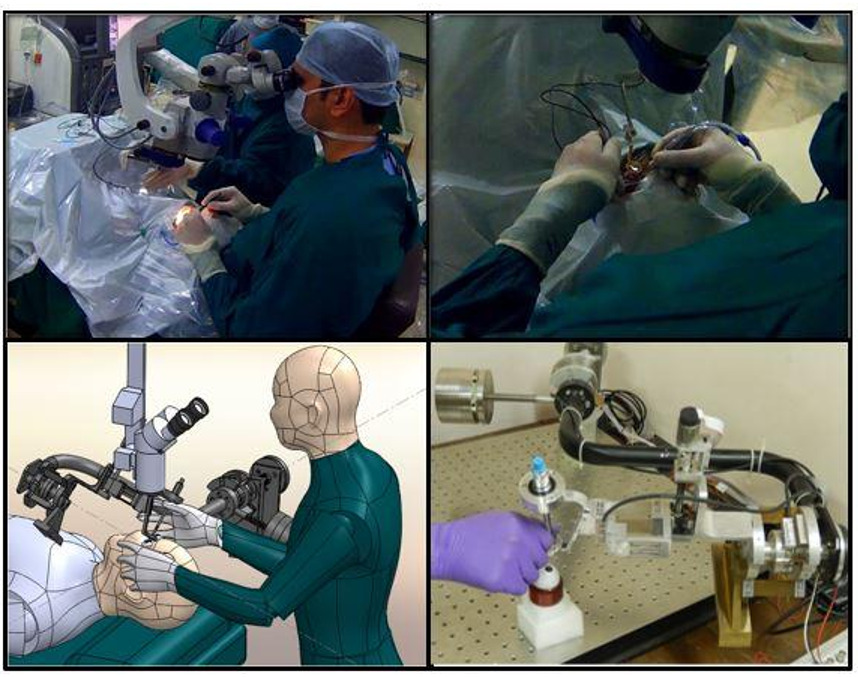
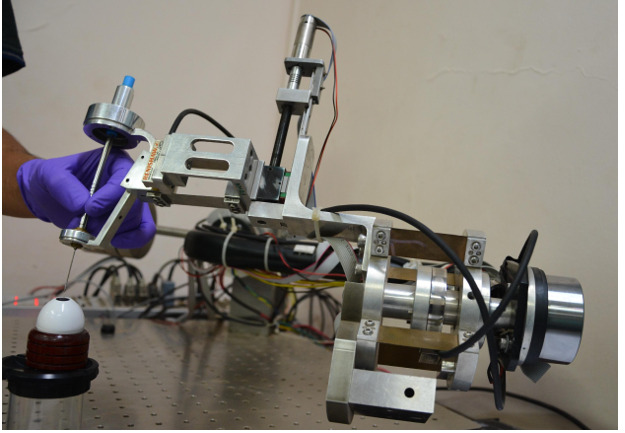
The invention relates to a robotic surgical system for performing high-precision, minimally invasive surgeries (MIS). The system includes a robot manipulator with compliant force/torque sensors, enabling four active DOFs through a combination of direct-drive actuators and compliant mechanisms. It supports both cooperative and joystick-controlled surgical modes, allowing tremor-free and accurate tool manipulation while preserving tactile feedback. Compatible with existing surgical instruments, the platform reduces cost and complexity while improving safety and precision in MIS applications like retinal surgery.
Minimally invasive surgical (MIS) procedures often involve operating in highly constrained environments where surgeon hand tremors, limited dexterity, and lack of tactile feedback reduce procedural accuracy and safety. Existing robotic systems for MIS are expensive, bulky, and heavily reliant on joystick-based control, which removes the natural feel of surgery and requires extensive training. These systems are also not readily adaptable for cooperative use or for deployment in cost-sensitive and rural settings. There is a need for a robotic surgical platform that provides high-precision motion, tremor-free actuation, and intuitive force feedback, while supporting both cooperative and teleoperated modes using standard surgical tools.
- Dual-Mode Surgical Operation: The platform enables both joystick-based teleoperation and cooperative surgeon-robot interaction, allowing for flexible surgical control while maintaining tactile engagement.
- Compliant Force-Sensing Mechanism: Compliant torque and force sensors are integrated into all active degrees of freedom, providing accurate force feedback without requiring modifications to existing surgical tools.
- High Precision with Tremor Cancellation: The use of backlash-free, direct-drive actuators combined with compliant mechanisms results in ultra-precise tool motion while effectively suppressing surgeon-induced tremors.
- Compatible with Standard Surgical Tools: The system accommodates unmodified surgical instruments, enabling easy integration into current surgical setups and reducing cost and training overhead.
- Modular and Scalable Platform: The robotic system is designed with modular actuation and sensing assemblies, allowing adaptation to various minimally invasive surgical procedures, including ophthalmic and retinal surgeries.
The prototype is a 4-degree-of-freedom (4DOF) surgical robotic system comprising an actuation unit with direct-drive motors, a compliant tool-holding end-effector, and a control console with force-sensing capabilities. The robot is designed for cooperative and teleoperated minimally invasive procedures, particularly retinal microsurgery. It allows intuitive manipulation by the surgeon and delivers high positional accuracy with tremor-free motion. The system has been successfully tested on dummy eye models to validate performance and stability under simulated surgical conditions.
A fully functional lab-scale prototype of the 4DOF compliant surgical robotic assist has been developed, integrating direct-drive actuators, compliant mechanisms, and precision encoders. The system has undergone detailed mechanical, electronic, and control integration and has been successfully tested on dummy eye models for retinal surgeries using a cooperative control strategy. Experimental results have demonstrated sub-degree accuracy, tremor suppression, and surgeon-controlled tool manipulation with surgical feel preserved. The design is validated, and the system is ready for advanced preclinical testing and potential translational development.
4
The technology enables high-precision, minimally invasive surgeries such as retinal procedures, enhancing surgical outcomes and reducing patient trauma. It supports cooperative and teleoperated modes, making advanced surgical care accessible in remote or underserved areas. By eliminating the need for tool-specific modifications, it offers a cost-effective and scalable solution for improving healthcare delivery.
- Retinal microsurgery and ophthalmology: Robotic system enables tremor-free, high-precision tool manipulation suited for delicate procedures like intravitreal injections and subretinal therapies.
- Precision drug delivery and gene therapy: Platform provides fine motor control for accurately administering therapeutics in targeted retinal regions, essential for emerging gene therapy techniques.
- Cooperative surgical robotics in rural clinics: Modular and cost-effective design supports deployment in low-resource settings, allowing surgeons to perform assisted procedures with reduced technical complexity.
- Surgical skill training and assistive technologies: System's cooperative mode with force feedback can aid novice surgeons in developing precision skills and reduce fatigue during extended procedures.
- Research in robotic systems for MIS: Platform serves as a testbed for advancing robotic control strategies, compliant actuation, and cooperative interface design in minimally invasive surgery.
- Medical instrumentation and prosthetic tool development: System's compatibility with standard surgical tools enables iterative development and testing of new instruments and surgical tool adapters.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
201911001356
554978