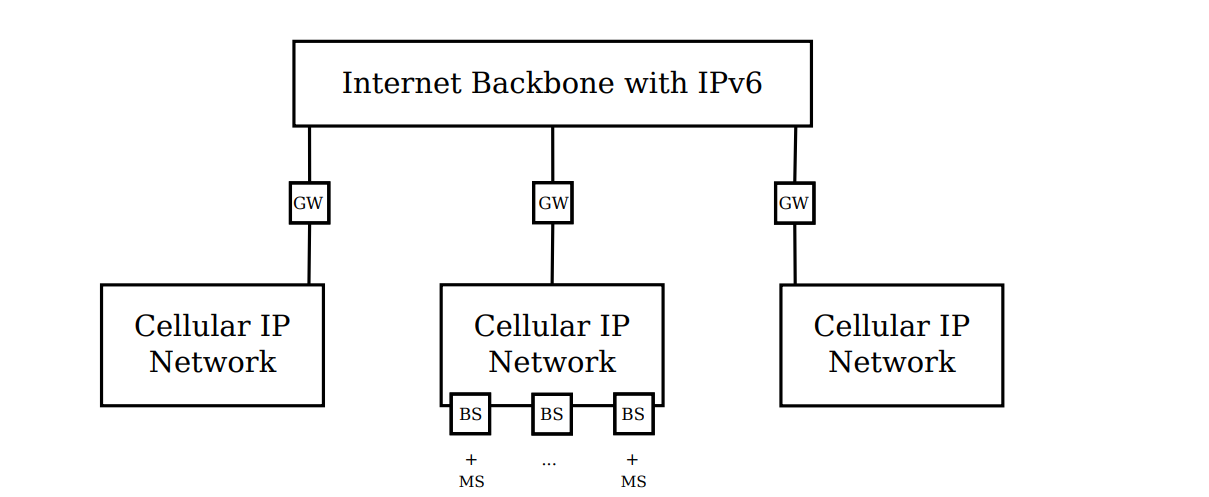
This invention presents a next-generation IP-based distributed cellular network architecture that overlays low-power pico base stations (pico-BSs) over existing high-power macro base stations (macro-BSs). The architecture introduces decentralized, scalable, and efficient network routing mechanisms using IPv6. By dynamically associating mobile hosts (MHs) with nearby pico-BSs and employing intelligent controllers (Regional Controllers and Pico-BS Controllers), the system significantly improves throughput, reduces handoff latency, and minimizes packet loss. The invention also introduces innovative signaling and routing methods like CoA Association Packets and Route Update Packets for seamless mobility and optimized network performance.
Conventional cellular networks struggle with packet loss, high signaling overhead, and latency during frequent handoffs, especially in dense or fast-moving user environments. Centralized architectures limit scalability and performance. There is a need for a decentralized, efficient, and scalable network model to ensure seamless mobility and improved data handling.
- Overlay of Pico-BSs on Macro-BSs: The architecture deploys low-range pico base stations within macro cell coverage areas to improve localized throughput and reduce macro BS load.
- Distributed IPv6 Architecture: It enables packet-switched, distributed control using IPv6 addressing, with dynamic assignment of Care-of Addresses (CoA) and Home Addresses (HoA) for seamless user mobility.
- Smart Controllers and Mobility Management: It incorporates Pico-BS Controllers, Regional Controllers, and a Central Control Gateway (CCGW) to manage mobility, authentication, routing, and address assignment.
- Efficient Handoff Mechanism: It implements a novel handoff method using Route Update and CoA Association Packets, enabling zero packet loss and low-latency transitions between base stations.
- Scalability and Load Distribution: By leveraging smaller cell sizes and decentralized control, the system is scalable and supports more users with better bandwidth utilization and reduced operational cost.
A simulation-based prototype of the distributed IP cellular architecture was developed using network modeling tools. It incorporated components like pico base stations, macro base stations, regional controllers, and mobile hosts with IPv6 addressing. The prototype successfully demonstrated dynamic handoff, address mapping, and seamless packet routing with zero packet loss. Performance was evaluated under varied user mobility scenarios, confirming improvements in throughput and reduced signaling overhead. The system architecture was validated for scalability and reliability in high-density environments.
The patent has already been granted by the Indian Patent Office. The process is well-defined and technically complete, with detailed system design and functional workflows. It is ready for prototyping and integration.
3
The proposed architecture enables affordable, high-speed, and resilient mobile connectivity, especially in densely populated or underserved areas. By decentralizing cellular infrastructure and minimizing packet loss, it supports real-time communication, emergency services, and digital inclusion. This technology empowers telecom providers to deliver better service with reduced costs, and aligns with the global push toward smart cities, ubiquitous connectivity, and next-generation internet infrastructure.
- Used by mobile network operators to improve coverage, capacity, and efficiency in 4G/5G networks
- Integrated into smart cities to support connected infrastructure like surveillance, traffic management, and public Wi-Fi
- Deployed in disaster recovery and remote areas for rapid communication setup with minimal infrastructure
- Supports large-scale IoT and machine-to-machine communication for industries and sensor networks
- Applied in enterprise campuses, stadiums, malls, and transport hubs to enhance localized connectivity
- Suitable for defense and tactical operations where secure and flexible mobile networks are essential
Geography of IP
Type of IP
1664/MUM/2012
371439