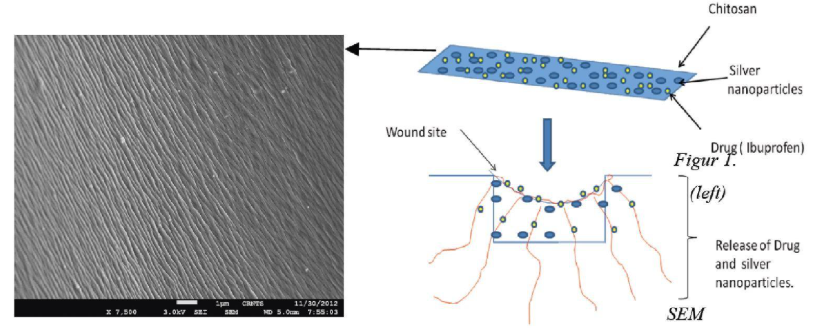
The present invention provides a wound dressing composition with antimicrobial, pain relieving, nontoxic, non-allergic, non-adherent, wound healing and hydrating properties. More particularly, the present invention relates to a wound dressing composition comprising a biopolymer matrix, a plurality of metal nanoparticles and a plurality of analgesic drug molecules and a method for preparing the same.
Despite the known biomedical benefits of chitosan, existing solutions have not effectively utilized it to develop a wound dressing that simultaneously offers antimicrobial action which don’t develop bacteria with resistance, pain relief, non-toxicity, non-allergenicity, non-adherence, and hydration with high absorption capacity. There is a need for a multifunctional wound dressing that offers antimicrobial protection without resistance, minimizes pain and trauma, and supports faster, safer wound healing.
- Synergistic Antimicrobial Effect: It utilizes a low concentration of metal nanoparticles (e.g., silver) in synergy with chitosan to reduce bacterial load effectively, minimizing the risk of resistance in microbes and side effects.
- Triple-Action Therapeutic Effect: The invention combines antimicrobial, analgesic (pain-relieving), and wound-healing properties in a single dressing composition.
- High Absorbency: Chitosan-based gel matrix exhibits a swelling ratio of up to 2500%, ensuring high water retention and effective absorption of wound exudates.
- Controlled Local Drug Delivery: The composition allows for localized, sustained release of metal nanoparticles and analgesic drug molecules at the wound site upon contact with exudate.
- Biocompatibility and Safety: The formulation is non-toxic, non-allergic, and non-adherent that minimizes patient discomfort and promotes healing without damaging surrounding healthy tissues.
- Stimulates Natural Healing: Biopolymers in the matrix promote dermal regeneration by stimulating macrophages, attracting neutrophils, and enhancing granulation tissue formation and re-epithelialization.
The present invention discloses a process for preparing a multifunctional wound dressing composition comprising a biopolymer matrix entrapping both metal nanoparticles and analgesic drug molecules. The process involves dissolving the biopolymer (such as chitosan or its derivatives) in a buffer solution to form a homogenous gel, followed by the addition of analgesic drugs and the preparation and incorporation of metal nanoparticles (e.g., silver or zinc). These components are uniformly dispersed and entrapped within the biopolymer matrix. The metal nanoparticles can be synthesized via methods like polyol reduction or hydrothermal processes. The final composition may be formulated into various dosage forms such as gels, sprays, or patches.
Technology was evaluated in-vitro and ex-vivo; no clinical studies were done and not evaluated beyond proof-of-concept.
5
The wound dressing composition significantly enhances patient care by reducing pain, minimizing infection risk, and accelerating healing, especially in chronic and burn wounds. By using lower concentrations of metal nanoparticles effectively, it reduces the risk of antimicrobial resistance and side effects, making advanced wound care more accessible and affordable.
- Healthcare
- Pharmaceuticals
- Medical Devices
- Wound Care
- Biomaterials
- Biotechnology
Geography of IP
Type of IP
2969/MUM/2014
434280