A new circuit design for converting single-phase AC power to DC power has been developed to smooth out the double-line-frequency power fluctuations inherent in single phase systems. Instead of using a large capacitor on the DC side, this invention adds a low power decoupling circuit at a high-frequency stage. By handling only a fraction of the fluctuating portion of the power, it uses smaller parts, extends component life, and delivers steady DC output idea as required in electric-vehicle chargers, solar inverters, etc.
In single-phase AC to DC power converters like those used in electric vehicle (EV) chargers or solar systems, there is a common issue of fluctuating power. This fluctuation causes high stress on the constituent devices, reduces the overall efficiency and requires bulky capacitors that wear out quickly, which can reduce the system’s lifespan. An intelligent, compact, and high-lifetime solution is needed.
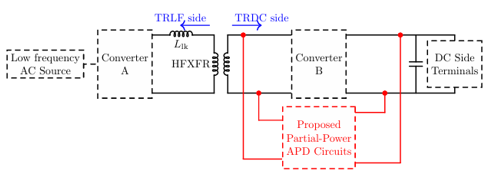
- Partial Power Handling: This invention is designed to ingeniously divert the ripple power to a capacitor based decoupling circuit. This circuit is operated in such a way that full ripple power compensation is achieved even while the decoupling circuit itself processes a fraction of the total ripple power. This feature helps in reducing the overall size and cost.
- High-Frequency Location: In this invention, the decoupling circuit is placed at the at a high-frequency link instead of the DC output port.
- Differential Capacitor Connection: Through a unique differential connection, the decoupling capacitor is operated at a higher voltage than the DC bus, which reduces the required capacitance and also the stress on the main component.
- Flexible Converter Topologies: This design works with either full-bridge or half-bridge switching stages, giving manufacturers simple options to match their cost and performance needs.
- Soft-Switching Capability: The implemented operational and control methods allow switches to turn on and off with minimal voltage stress, slashing thus lowering switching losses and heat generation.
The invention exists as a detailed computer model. Simulations at 230 V, 50 Hz input and 3.45 kW output show stable DC voltage, smooth currents, and a large drop in peak power handled by the partial power decoupling circuit. End-to-end open loop and closed loop circuit simulations and desired results have been established in software.
The technology has been successfully demonstrated using computer-based simulations, showing promising results for reducing power fluctuation and improving efficiency. Hardware development and testing is currently in progress.
4
Compact and durable single stage single phase bidirectional AC-DC converters such as the one presented in this invention are promising candidate topologies for EV chargers and solar inverters as they offer more reliable and efficient solutions. There can be a potential reduction in operational costs and electronic waste generation for such converters. By enabling a smart and efficient power conversion product, consumer convenience can be emphasized thereby elevating their confidence in electric vehicles and renewable installations. As more people and businesses make the switch, we can drive down fossil-fuel use using products such as the one in this invention, curb carbon emissions, and move closer to a truly sustainable energy future.
- Electric-vehicle charging stations
- Solar and wind power inverters
- Vehicle-to-grid bidirectional chargers
- Industrial motor drives
- Off-grid power systems
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202421042870
562145