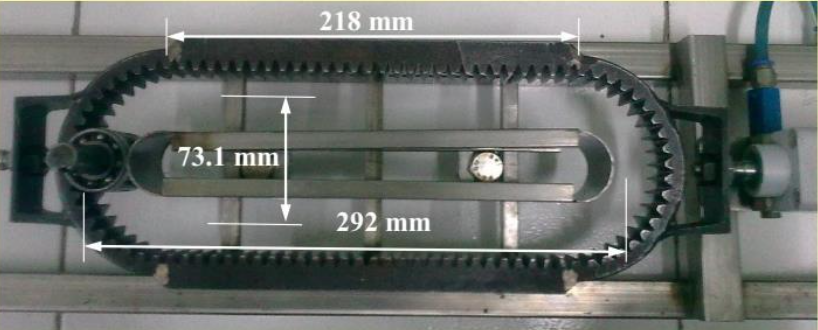
This innovation is an apparatus for converting rotary motion to reciprocating motion and vice versa using an enclosed reciprocating rack and a rotatable circular element. The rack is formed by two elongated members and two end connecting members, all featuring internal teeth. A circular gear with external teeth engages these internal teeth to enable continuous motion conversion. The system includes a locking or latching mechanism to maintain constant engagement between the gear and rack. This ensures smooth, efficient, and precise motion transmission. The design supports bi-directional operation and minimizes mechanical wear.
Conventional mechanisms to convert reciprocating motion to rotary motion and vice versa, for example, the slider crank mechanism, suffer from limitations such as restricted stroke-to-bore ratios, bulky and heavy design, and issues with vibrations and wear due to unbalanced forces. These shortcomings lead to inefficiencies, uneven wear, and potential fluid leakage.
There is a need for a more efficient mechanism to convert reciprocating motion to rotary motion and vice versa that enables longer strokes independent of bore diameter, while minimizing wear and mechanical imbalance.
- Enclosed Reciprocatable Rack with Internal Teeth: The system includes a rack composed of two elongated straight members and two end members forming an enclosed structure. All sides feature internal teeth to allow 360° interaction with a rotatable circular element for efficient motion conversion.
- Advanced Locking Mechanism: Multiple locking solutions—permanent magnets, latching cylinders, cam-follower systems, and roller-guide assemblies—ensure the circular element remains engaged with the rack teeth at all times, reducing backlash and enhancing operational stability.
- Longer Strokes Independent of Bore Diameter: The mechanism enables direct linear motion through gear-rack interaction, allowing for significantly longer strokes without being constrained by bore diameter, unlike traditional crank-slider systems.
- Reduced Wear and Improved Efficiency: With minimized side forces, balanced motion, and continuous positive engagement, the system reduces friction, wear, and mechanical imbalance—resulting in smoother operation and higher efficiency.
The prototype consists of an enclosed reciprocatable rack made from two elongated linear members and two connecting end members, all featuring internal teeth. A rotatable circular element with external teeth engages sequentially with these internal teeth to convert rotary motion to reciprocating motion and vice versa. The circular element is mounted on a central shaft that passes through vertically oriented plates positioned adjacent to the rack. A locking mechanism—comprising magnets, latching cylinders, cam-follower systems, or roller-guide assemblies—ensures constant engagement between the gear and rack. In some configurations, rollers mounted on arms guide the gear through dedicated guide-ways, maintaining precise alignment.
The mechanism was fabricated and integrated as the drive for long-stroke reciprocating steam compressors and operated successfully to enable energy saving in the jaggery-making process.
4
This invention improves mechanical efficiency and durability, reducing maintenance and energy loss. Its compact design supports space-saving innovations in automation and robotics. By enabling longer strokes with less wear, it enhances reliability across industries. Overall, it promotes sustainable and cost-effective engineering solutions.
- Air Compressors and Expanders
- Steam Compressors and Expanders
- Two-Phase Vapour Compressors and Expanders
- Heat Pumps
- Industrial Dryers
- Automobiles
- Robotics
- Industrial Automation
- Manufacturing Equipment
- Aerospace
- Defence
Geography of IP
Type of IP
1847/MUM/2014
366628