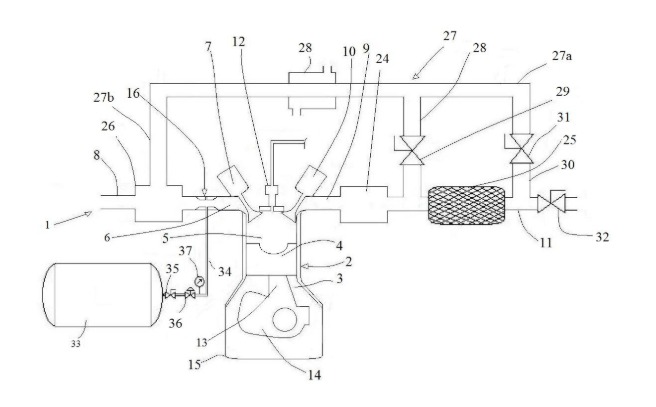
The dual fuel compression ignition internal combustion engine system integrates Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) and diesel to leverage the strengths of both fuels. This innovative system uses a Reactivity-Controlled Compression Ignition (RCCI) approach, combining a low reactivity fuel (CNG) with a high-reactivity fuel (diesel) for optimal combustion. The engine features an advanced Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system, including a catalytic converter and gas cooler, to reduce harmful emissions such as NOx and Particulate Matter (PM) while maintaining high brake thermal efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate significant reductions in emissions without compromising engine performance, making this technology ideal for applications in automotive, heavy-duty transportation, marine engines, agricultural machinery, and power generation.
Compression ignition engines offer a better thermal efficiency and produce less greenhouse gasses. However, simultaneous reduction in NOx and Particulate Matter (PM) emissions is a major challenge with the compression ignition engines.
Some advanced combustion modes, such as homogeneous charge compression ignition, premixed charge compression ignition, low temperature combustion etc., offer viable solution to reduce NOx and PM simultaneously for narrow operating range (no load to part load). However, these advanced combustion techniques produce an unacceptable amount of HC and CO emissions. Also, achieving these combustion modes at full load is still a challenging task.
- Dual Fuel Compression Ignition Internal Combustion Engine System: The engine uses a combination of CNG and diesel, where CNG is premixed with intake air and diesel is directly injected, in a Reactivity-Controlled Compression Ignition (RCCI) engine. This allows efficient combustion and significant emission reductions.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR): This innovation incorporates a sophisticated EGR system with a catalytic converter and gas cooler, improving the efficiency of exhaust treatment and reducing NOx emissions.
- Optimized Injection Strategy: It offers multiple injection strategies for diesel to ensure optimal combustion, even at varying engine loads, thereby maintaining high brake thermal efficiency while lowering NOx, PM, hydrocarbons, and carbon monoxide emissions.
- Emission Reductions: This solution achieves substantial reductions in NOx and PM while maintaining acceptable levels of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide.
- High Brake Thermal Efficiency (BTE): It maintains or improves engine efficiency compared to traditional single-fuel engines.
The prototype engine includes a combustion chamber, air intake manifold, exhaust manifold, diesel injector, CNG injector, and an EGR loop with a catalytic converter and gas cooler. The system operates with varying CNG and diesel ratios, demonstrating optimal performance with a 10% CNG and 90% diesel mixture. Experimental results showed reduced NOx and PM, maintained acceptable HC and CO levels, and achieved high BTE.
- The Dual Fuel Compression Ignition Internal Combustion Engine System, which employs both CNG and Diesel, represents a significant advancement in automotive technology.
- This system leverages the high energy density of diesel for ignition while utilizing the cleaner-burning properties of CNG to reduce overall emissions and improve fuel efficiency.
- Recent developments have focused on optimizing fuel injection strategies, combustion chamber design, and electronic control systems to seamlessly integrate the dual fuels. As a result, these engines are becoming increasingly attractive for both environmental and economic reasons, offering a viable solution for reducing the carbon footprint of heavy-duty and commercial vehicles.
Demonstration and validation in the lab environment
Reducing emissions from internal combustion engines can significantly lower the emissions impact to the environment, contributing to better air quality and public health. It also supports global efforts towards sustainable and eco-friendly transportation.
- Automotive Engines: Passenger cars and commercial vehicles
- Heavy-duty Vehicles: Trucks, buses, and construction equipment
- Marine Engines: Ships and boats requiring high efficiency and low emissions
- Agricultural Machinery: Tractors and other farming equipment
- Power Generation: Engines used in generators and backup power systems
Geography of IP
Type of IP
3009/MUM/2014
413535