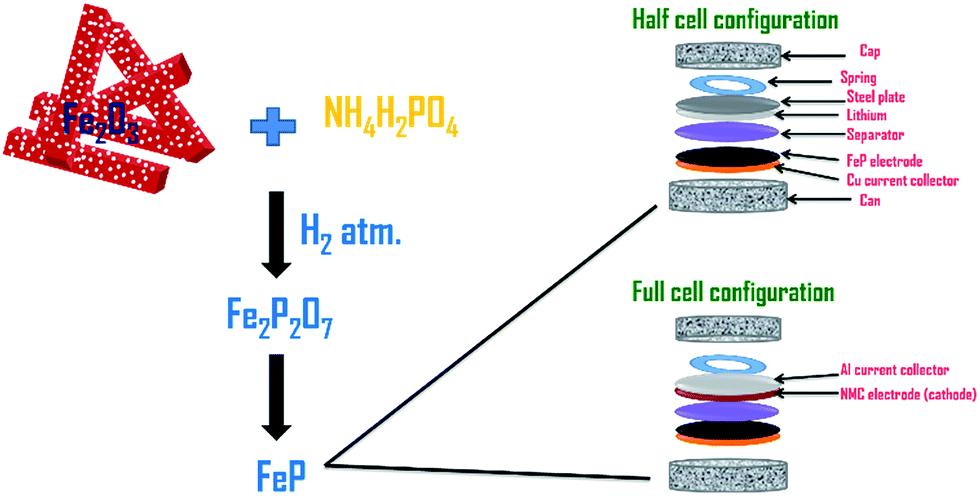
This research investigates Ferric oxide porous nanostructures as a high-rate capable anode material for lithium-ion batteries. The Ferric oxide anodes demonstrate exceptional capacity and cycling stability, offering a promising alternative to traditional graphite anodes.
Lithium-ion batteries power our everyday lives, from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles. However, current battery technology faces limitations. The most commonly used anode material, graphite, has a limited capacity, meaning batteries run out of power faster and require frequent charging. Additionally, traditional battery production methods can be expensive and raise safety concerns.
- The Ferric oxide porous nanostructures have a high theoretical capacity of 1007 mAh/g, exceeding the capacity of commonly used graphite anodes. Half-cell testing confirms this advantage, delivering a reversible capacity of 903 mAh/g at a 1C rate.
- Full-cell testing, using both the Ferric oxide anode and a LiCoO2 cathode, demonstrates exceptional stability. The cell retains 91% of its capacity after 100 cycles, even at a demanding 1C rate. This translates to a maintained capacity of around 800 mAh/g, highlighting the material's ability to endure repeated charging and discharging cycles with minimal capacity loss.
- The porous nanostructure design allows the Ferric oxide anode to deliver excellent rate capability. The material can handle high current densities (5C rate) while maintaining efficient lithium-ion storage.
- Ferric oxide is a readily available and cost-effective material compared to some alternatives. Additionally, the potential for using water-based binders in the fabrication process opens doors for further cost reduction and improved safety by eliminating the need for flammable organic solvents.
Pouch cells fabricated with Ferric oxide anode successfully power a solar study lamp and ultra-bright LED array.
4
The development of high-performance, cost-effective, and safer lithium-ion batteries supports sustainable energy storage solutions.
Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), batteries, grid storage, consumer electronics, and wireless devices.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
201621027395
396467