This invention is a new type of solar energy receiver that can capture and convert sunlight into heat more efficiently than existing designs. It uses a cavity filled with hollow plates to absorb concentrated sunlight. Heat transfer fluid, which can be a gas, liquid, or even change state during the process, flows through these plates and carries the collected heat away.
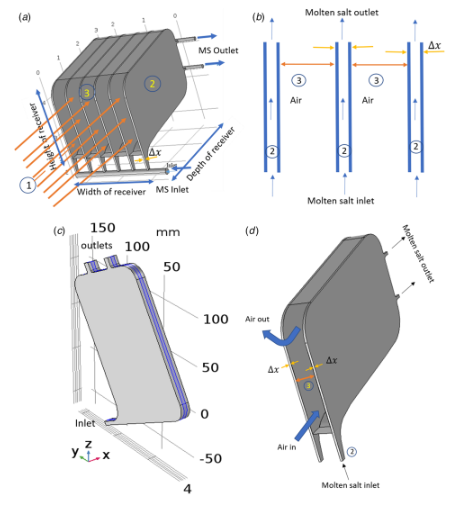
Figure 1. The geometry of the Plated Volumetric Cavity Receiver: (a) molten salt volumetric plated cavity receiver, (b) flow mechanism inside the receiver, (c) hollow plate (all dimensions in m), and (d) heat loss mechanism
[Ref: Singh, O., Bhatwadekar, K., Kartheek, N. G., Kedare, S. B., and Singh, S. (July 28, 2020). "A Novel Design of Liquid Volumetric Plated Cavity Receiver for Central Tower Systems." ASME. J. Sol. Energy Eng. February 2021; 143(1): 011009. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4047669 ]
Current volumetric cavity receivers in solar energy plants are limited in the type of heat transfer medium they can effectively utilize. Traditionally, only atmospheric air works well. Unfortunately, non-transparent, pressurized, or high-density fluids, which offer potential advantages, require additional covers or intricate setups, making them impractical for many applications. This significantly restricts the flexibility and efficiency of current cavity receiver technology.
- Volumetric design: The receiver uses a cavity with multiple hollow plates exposed to concentrated sunlight, maximizing heat transfer efficiency.
- Flexible arrangement: Plates can be arranged vertically, horizontally, or inclined for optimal light capture.
- Sliding supports: These supports allow for thermal expansion and contraction, reducing stress on the system.
- Internal flow management: Flow regulators and spacers in the hollow plates optimize heat transfer fluid flow.
- Versatile heat transfer mediums: The design supports various liquids, gases, and supercritical CO2, offering more flexibility.
- Improved efficiency: The design promotes efficient heat transfer and maximizes solar energy capture.
- Reduced thermal stress: Sliding supports minimize thermal stress, enhancing durability.
NA
The technology is under research and development phase. Initial simulations and theoretical analyses have demonstrated promising results, indicating potential for higher efficiency compared to conventional systems.
3
This invention has the potential to increase the efficiency of solar energy capture by :
- Reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions,
- Providing a cleaner and more sustainable energy source, and
- Potentially lowering the cost of solar energy production.
- Solar power plants: It can enhance the efficiency of heliostat tower configurations and dish concentrators in solar thermal energy generation.
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems: It can be used for implementing solar-driven HVAC systems for large buildings and industrial complexes.
- Energy storage: It can be integrated with thermal energy storage systems to store and dispatch solar energy efficiently.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
201721005417
462835