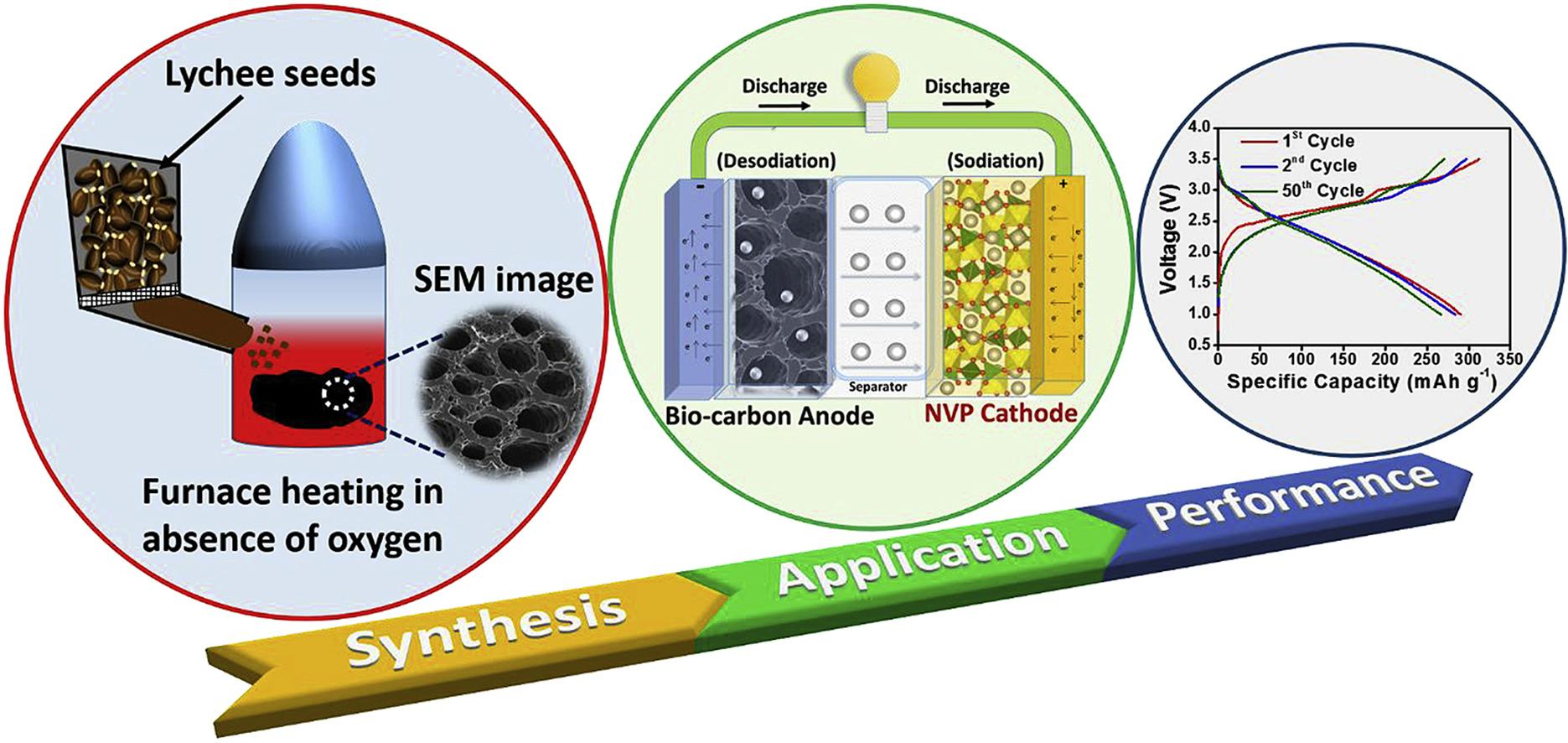
This invention addresses the limitations of current sodium-ion battery technology by introducing a novel bio-derived carbon anode material. This low-cost, easily synthesized material offers excellent performance, paving the way for a more sustainable and affordable energy storage solution.
The world's increasing reliance on electronics and renewable energy sources demands efficient and affordable energy storage solutions. Lithium-ion batteries, currently dominating the market, are facing challenges due to the limited availability and rising cost of lithium. Sodium-ion batteries offer a promising alternative but are currently hindered by the complexity and high cost of producing key components, particularly anode materials like hard carbon.
- Sustainable solution: Bio-derived carbon anode material from lychee seeds offers a readily available, cost-effective alternative to hard carbon anodes.
- Simplified synthesis: The bio-carbon anode synthesis involves a low-temperature process (500°C) without the need for an inert atmosphere, significantly reducing production costs to approximately $3/Kg compared to $5-15/Kg for hard carbon.
- Cost reduction: By eliminating expensive additives and surface modification techniques, the overall cost of the sodium-ion battery technology is reduced.
- High performance: The sodium-ion full cell demonstrates an energy density of 200 Wh/kg at a current density of 100 mA/g, making it a viable alternative for practical applications.
Anode: Bio-derived carbon as the active material, with Super C65 conducting additive and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) binder.
Cathode: Sodium vanadium phosphate (Na3V2(PO4)3) as the active material, Super C65, and PVDF binder.
Separator: Borosilicate glass fiber soaked in 1M NaClO4 with 3 wt% fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) electrolyte.
Functional sodium-ion battery prototype using bio-derived carbon anode and Na3V2(PO4)3 cathode delivers an energy density of 200 Wh/kg at a current density of 100 mA/g.
Functional sodium-ion battery prototype using bio-derived carbon anode and Na3V2(PO4)3 cathode delivers an energy density of 200 Wh/kg at a current density of 100 mA/g.
5
This technology could revolutionize energy storage by providing a low-cost, sustainable alternative to lithium-ion batteries. Widespread adoption of sodium-ion batteries can facilitate the transition to renewable energy sources.
- Grid-scale energy storage
- Stationary energy storage
- Renewable energy storage
- Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Consumer electronics
Geography of IP
Type of IP
201841036449
413867