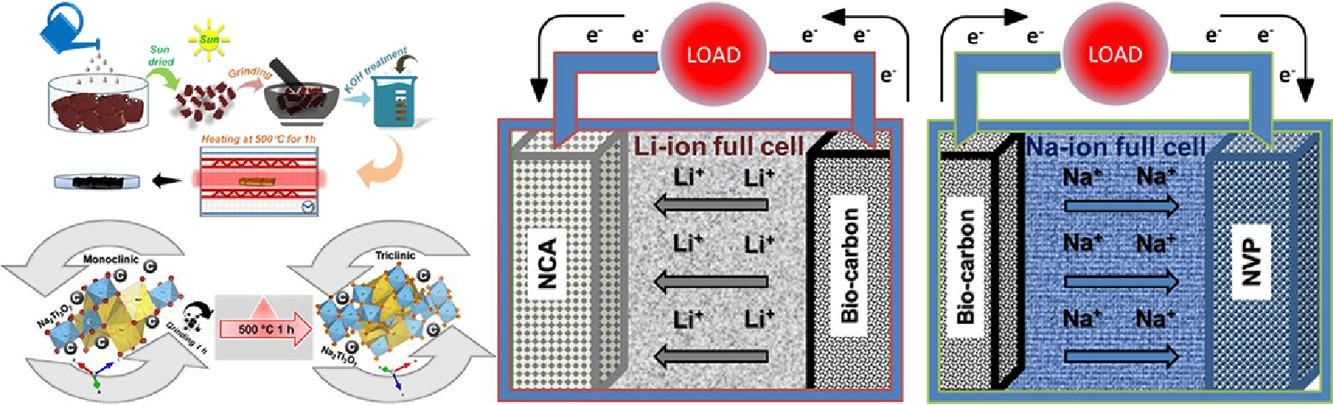
This invention introduces a method for synthesizing bio-derived carbon from Tamarindus Indica seeds and its composite with sodium titanates (NTO) for use as anodes in sodium-ion batteries (SIBs). The process involves a cost-effective, scalable approach that leverages sustainable sources to produce high-performance anode materials, thereby enhancing the efficiency and reducing the cost of SIBs.
Lithium-ion batteries are the most common rechargeable battery today, but lithium is a limited resource. Sodium-ion batteries are a promising alternative because sodium is much more abundant, but current anode materials, such as graphite, do not perform adequately with sodium ions. There is a need for low-cost, high-performance anode materials that are also environmentally sustainable.
- This innovation utilizes Tamarindus Indica seeds as a bio-derived source for carbon.
- Powdered seeds are heated at controlled temperatures to produce bio-carbon.
- This technology combines bio-derived carbon with sodium titanates (NTO) to form a composite.
- Sodium-ion battery prototypes demonstrate excellent cyclic stability and specific capacity.
- This methodology is cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and scalable synthesis process.
- It utilizes abundant and renewable bio-materials.
- It shows improved electrochemical performance over traditional graphite anodes.
- It enhances the practicality and affordability of sodium-ion batteries.
Sodium-ion batteries using bio-derived carbon and NTO-BC composite anodes show high specific capacity (350 mAh/g for bio-derived carbon and 275 mAh/g for NTO-BC) and good cycle stability.
Sodium-ion batteries using bio-derived carbon and NTO-BC composite anodes show high specific capacity (350 mAh/g for bio-derived carbon and 275 mAh/g for NTO-BC) and good cycle stability.
5
This technology promotes sustainable energy storage solutions by reducing dependency on lithium, leveraging renewable resources, and potentially lowering the cost of battery production. It contributes to environmental conservation and supports the global shift towards renewable energy and electric mobility.
- Energy storage systems, especially where sodium-ion batteries are preferable
- Portable electronics requiring efficient and sustainable battery solutions
- Renewable energy storage, including solar and wind power systems
- Automotive industry, particularly for electric vehicles
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202121030174
478825