The invention proposes a new method for producing pouch cell housings used in batteries, particularly for electric vehicles and other electronic devices. The traditional deep drawing process is replaced with a vacuum forming method, allowing for greater stack heights and enhanced safety features like venting valves.
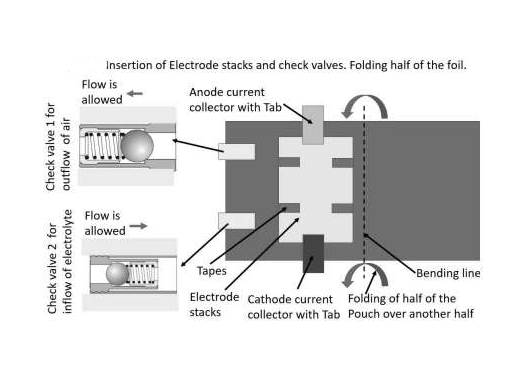
The conventional deep drawing process for creating pouch cell housings limits the height of the pouch due to cracks at the corners and wrinkles under the blank holder surface. This restricts the number of electrode-separator stacks that can be housed, impacting the capacity and efficiency of the battery.
- Vacuum forming method for pouch cell housing
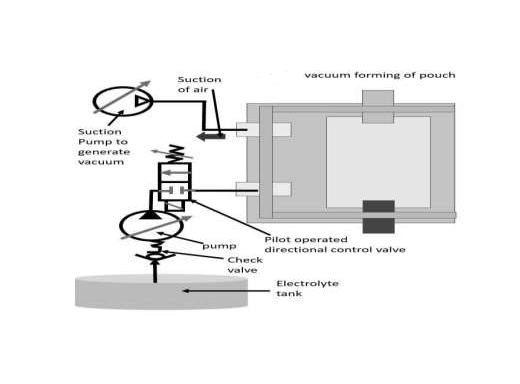
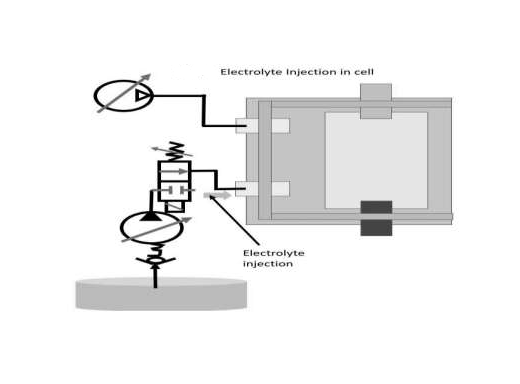
- Integration of four processes: placing stacks, sealing laminate, generating vacuum, and filling electrolyte
- Eliminates limitations of deep drawing by allowing for greater stack heights
- Incorporation of venting check valves to manage internal gas pressure
- More consistent electrolyte filling and wetting of electrodes
- Reduced risk of defects such as wrinkles and cracks
- Automated process for higher efficiency and lower cost
- Enhanced safety with venting valves to prevent thermal propagation
NA
The method has been proposed and detailed in technical documents. It includes conceptual illustrations and process descriptions, indicating a well-developed approach ready for prototyping and further testing.
2
This technology can lead to more reliable and safer battery packs, enhancing the performance and safety of electronic devices, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems. Improved battery quality and safety can contribute to broader adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions.
- Electric vehicles
- Renewable energy storage systems
- Electronic devices requiring rechargeable batteries
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202221053710
539312