This invention describes a new method for creating a thin layer of carbon-coated silicon-silicon carbide (Si-SiC@C) from black rice husk ash (BRHA) for use in rechargeable batteries, particularly lithium-ion batteries. The method is a single-step process that avoids the need for additional carbon sources or harsh chemicals, making it more environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
Currently used methods for creating silicon-silicon carbide (Si-SiC@C), a promising material for lithium-ion battery anodes, often involve multiple steps and additional resources. These extra steps can be expensive and create environmental concerns. Often, harsh chemicals like hydrofluoric acid are used, which are hazardous and require special handling and disposal. Additionally, these methods typically rely on separate sources for silicon and carbon precursors, increasing the complexity and cost of production.
- Single-Step Process: This innovative method offers a single-step process for the synthesis of Si-SiC@C composites, eliminating the need for intermediate steps and external carbon precursor sources.
- Utilization of Waste Material: By using black rice husk ash as a precursor, the process makes efficient use of a waste material, contributing to sustainability.
- Cost-Effective: The method involves moderate heating temperatures and utilizes ambient conditions, making it cost-effective compared to traditional approaches that may require specialized equipment and higher energy inputs.
- Environmentally Friendly: The use of hydrochloric acid (HCl) instead of hydrofluoric acid (HF) for purification enhances the environmental friendliness of the process.
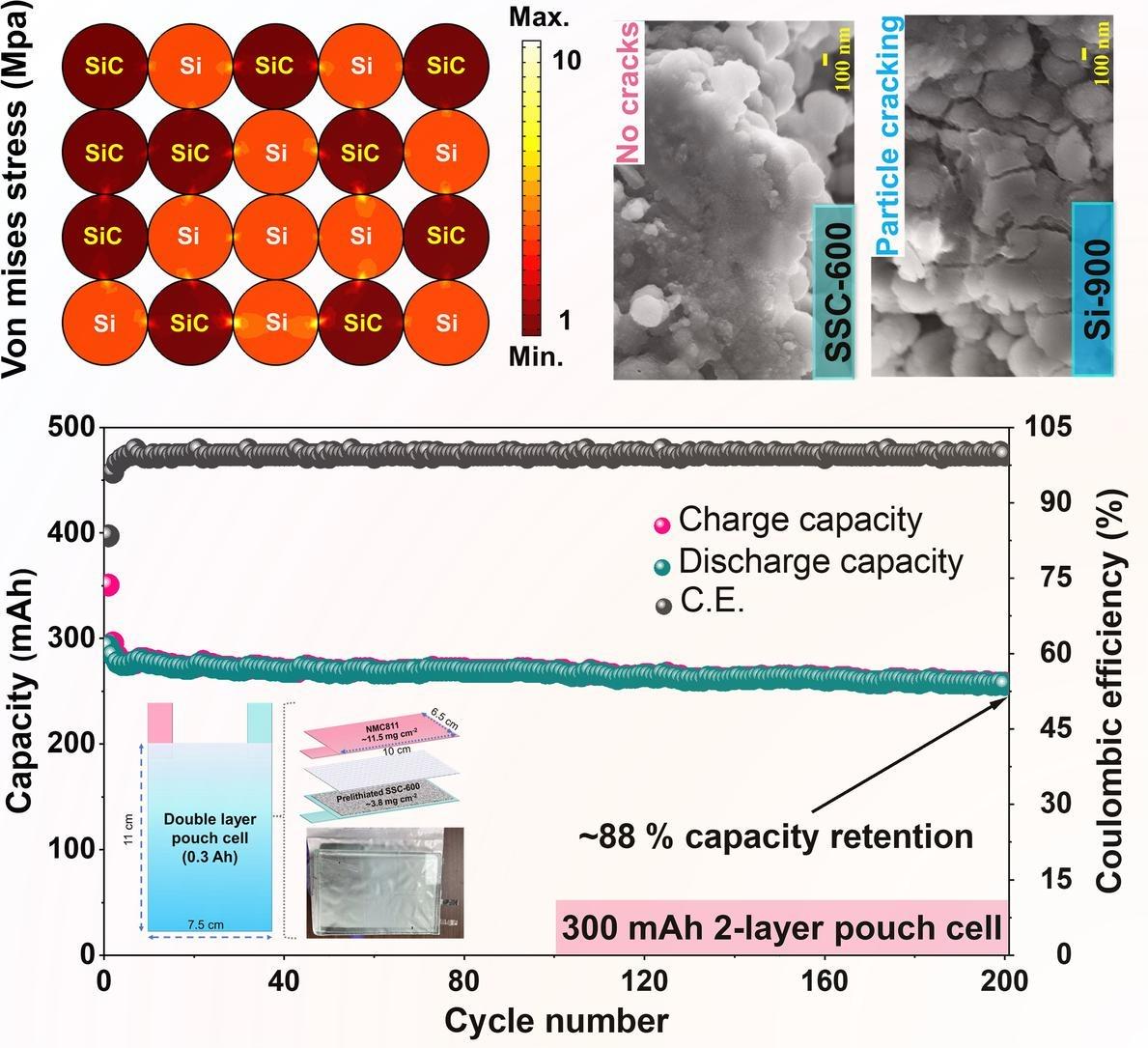
- High Areal Capacity: The resulting Si-SiC@C composite, when used as a negative electrode material, exhibits a high areal capacity of around 2 mAh cm^-2, indicating its potential for high-performance lithium-ion batteries.
- Cycling Stability: The negative electrode demonstrates excellent cycling stability, with up to 500 charge and discharge cycles, indicating the durability and reliability of the battery material.
NA
Significant progress has been made in developing a method for synthesizing carbon-coated silicon-silicon carbide (Si-SiC@C) composites from BRHA, with promising implications for lithium-ion battery technology.
4
This invention has the potential to improve the sustainability and cost-effectiveness of lithium-ion battery production. It could also lead to the development of new and improved battery technologies.
- Lithium-ion batteries
- Rechargeable batteries
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202221062575
438150