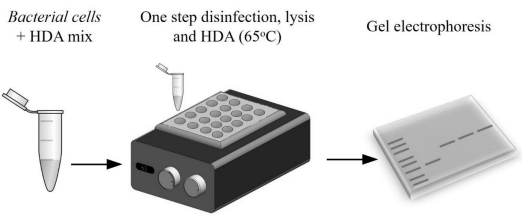
This invention provides a method and a device for the single-step disinfection, thermal lysis and isothermal amplification of nucleic acid from the target cell (particularly targeting Mycobacteria). It simplifies the detection process, making it highly efficient and suitable for point-of-care diagnostics by integrating both lysis and DNA amplification into one step at a consistent temperature of 65°C.
The current diagnostic methods for the amplification of nucleic acid are expensive, require multiple steps, and are not suitable for point-of-care settings, particularly in resource-limited environments. The existing methods typically involve complex processes like PCR that require costly equipment and multiple temperature cycling, which makes the entire processes time consuming and need expert operators to perform the test.
- Cost effectiveness: This innovation eliminates the need for expensive equipment like thermocyclers as it (i) combines thermal lysis and isothermal amplification into a single reaction step and (ii) operates effectively at 65°C utilizing helicase-dependent amplification, thus eliminating the need for a thermocycler.
- Simplicity: It eliminates the need for multiple steps and manual intervention, reducing potential errors and procedural complexity. The process is simplified by working effectively in the presence of cell debris, so no washing or purification is needed.
- Accessibility: It is suitable for point-of-care applications, enabling rapid, on-site diagnostic capabilities.
- Efficiency: It streamlines the process by removing the need for disinfection, cell washing or DNA purification, while maintaining high sensitivity and specificity.
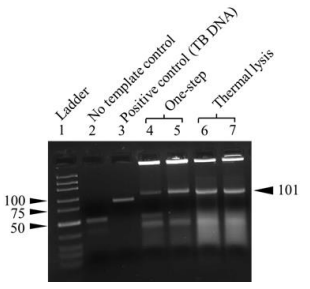
Proof-of-concept has been demonstrated.
A proof-of-concept has been demonstrated in the lab environment with cultured bacterial samples.
3
The diagnostics accessibility, and thereby healthcare accessibility, is greatly enhanced in remote areas. The costs of diagnostics are lowered significantly, allowing for more widespread testing. Also, faster diagnosis leads to quicker treatment initiation, potentially reducing transmission rates.
- Medical diagnostics: Particularly useful for rapid tuberculosis testing at the point-of-care, including remote or resource-limited settings
- Public health: Enables quick screening in epidemic situations and in regions of high incidence of disease-causing bacterium
- Research: Facilitates studies on various types of cells by simplifying sample preparation
- Forensic science
- Agriculture
Geography of IP
Type of IP
201621026481
400709