The present invention introduces a novel selection or access device for cross-point memory, specifically designed for bipolar memory technologies such as bipolar RRAM (Resistive Random-Access Memory) and STT RAM (Spin-Transfer Torque RAM). This device, featuring an ambipolar or selector component, addresses the challenge of current leakage in cross-point memory arrays by employing a two-terminal structure that operates at sub-0.5V, unlike traditional three-terminal transistors. This innovation enables higher density (1 transistor per cell) and faster switching suitable for SRAM replacement and neuromorphic circuits, enhancing power efficiency and scalability. The invention also includes methods of fabrication and pertains to a memory system incorporating this device, promoting its use in various memory applications and computational systems modeled after neuromorphic circuits.
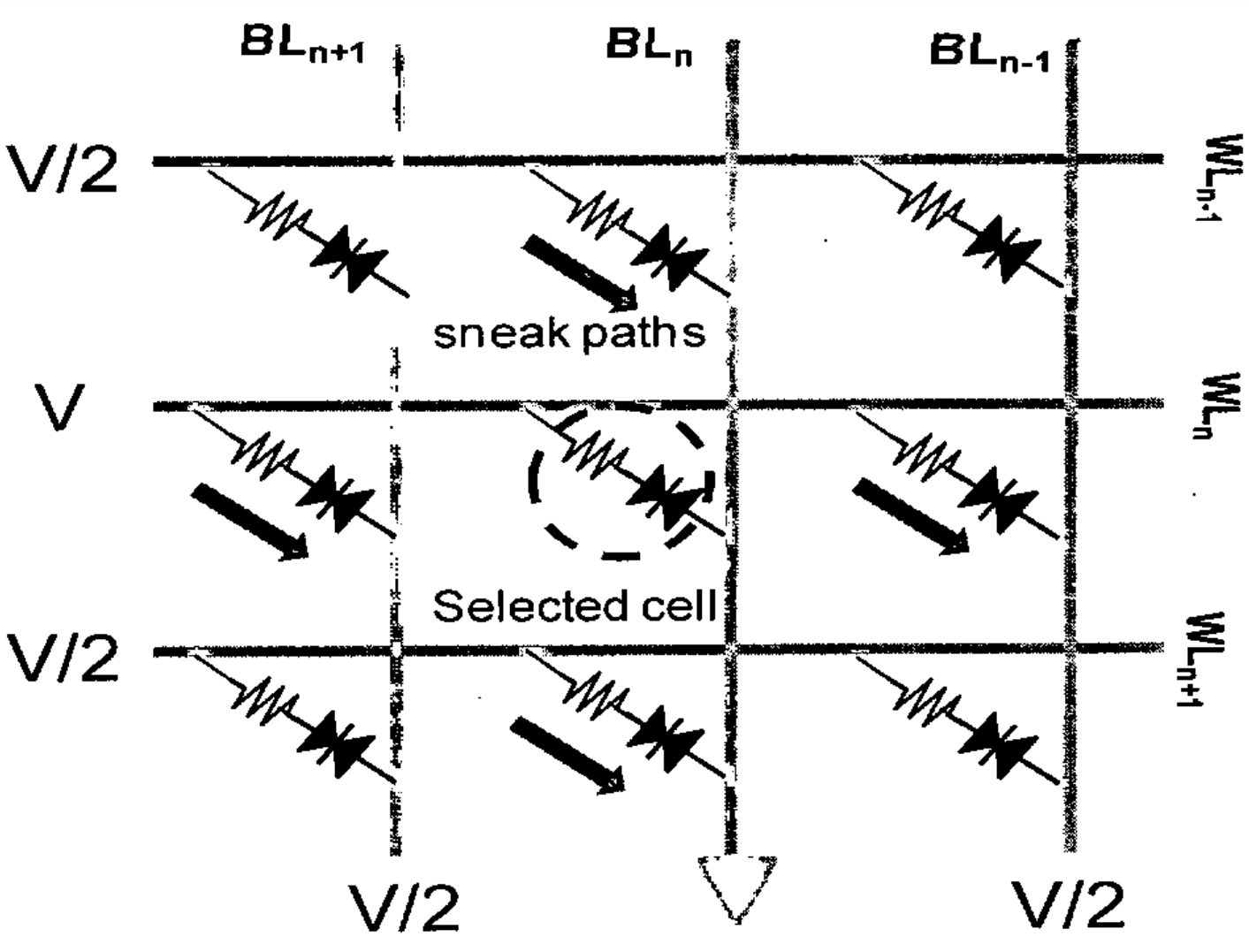
Cross-point memory arrays suffer from current leakage through unselected memory cells, which affects the reading and writing of the selected memory cells.
- Ambipolar selection device (NPN or PNP diode) with steep subthreshold slope due to impact ionization or band-to-band tunneling
- High on-current density (>10MA/cm²) and low turn-on voltage (<0.6V)
- High on-off current ratio (10⁴) with sub-threshold slopes up to 6mV/decade
- Simplified design for neuromorphic computing applications
- Two-terminal design enables integration with various memory technologies and neuromorphic circuits
- Reduced power consumption and increased memory density
- High-speed memory access and programming
- Compatibility with existing SRAM power supply (VDD)
- The prototype involves a two-terminal ambipolar selection device
- Uses materials like Si, Ge, C, Sn, and their alloys
- Demonstrates high on-current and low turn-on voltage with steep subthreshold slopes
- Prototype structures and doping profiles have been simulated and validated
An experimental demonstration of a bipolar selector device operating at low voltage with a high ION/IOFF ratio has been completed. Integration of the bipolar selector device with resistive random-access memory in a crossbar array for neuromorphic computing is ongoing.
- Improved efficiency and performance of memory devices
- Enhanced capabilities for neuromorphic computing, contributing to advancements in artificial intelligence
- Potential reduction in energy consumption for electronic devices
- Semiconductor manufacturing
- Memory technology - RRAM and STTRAM technologies
- High-density memory applications
- Neuromorphic computing systems
- Data storage solutions
- Consumer electronics - Low-power electronic devices
Geography of IP
Type of IP
2134/MUM/2013
422299