This invention addresses the problem by characterizing the stochastic Set in PCMO RRAMs, leveraging the device's internal state (resistance) and external input (voltage pulse) for control. This dual approach ensures consistent stochastic distribution across numerous iterations.
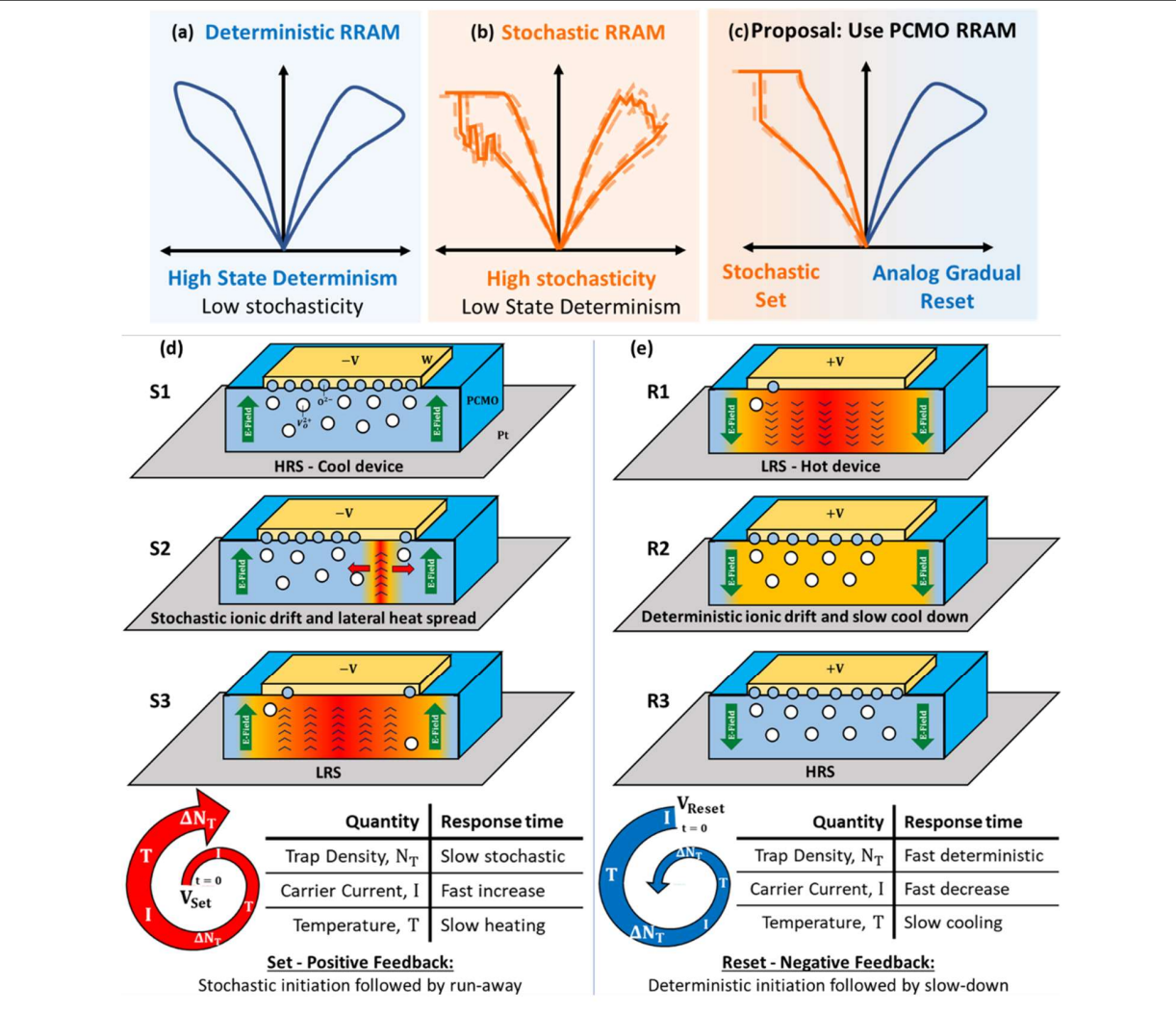
Figure 1. Proposed benefits of PCMO RRAM as a stochastic neuron: PCMO RRAM combines the features of (a) deterministic RRAM and (b) stochastic RRAM different polarities to demonstrate (c) stochastic Set and analog gradual Reset (d) Set and (e) Reset mechanisms for PCMO RRAM. Set process starts as a stochastic ionic drift followed by thermal run-away (positive feedback), Reset starts as a deterministic ionic drift followed by slow cooldown (negative feedback).
Emerging non-volatile memories like RRAMs, MRAMs, and FeRAMs have been proposed for a wide range of applications. However, controlling stochastic distribution over numerous iterations is challenging, especially as problem sizes scale, necessitating parametric control over stochasticity.
- Stochastic Set Time Measurement: This technology establishes a causal dependence on the initial high resistance state of the device.
- State-Monitored Stochasticity: It combines internal state and external input for stable stochastic distributions.
- Analog Reset Process: It ensures excellent internal state control.
- Drift Reduction: It achieves 100× reduced Set time distribution drift, improving Boltzmann Machine performance.
- Scalable Solutions: It is capable of solving problems 20× larger than conventional methods.
- Improved Performance: It provides 10× better performance by tuning out device-to-device variability.
- Consistency Over Time: It maintains reliable stochastic distributions over extended iterations.
- Device Used: Pr1-xCaxMnO3 RRAMs
- Key Features: Analog switching states, low device-to-device variability, scalable currents, and inherent stochasticity.
- Test Conditions: The device's performance was analyzed under various resistance states and voltage pulses to ensure consistent stochasticity.
Stochastic invariance control method has been demonstrated on individual devices (~10). Experimental switching characteristics have been used in software and proven to eliminate device and cycling variability for an optimization problem of upto 1000 nodes. A software-hardware hybrid network has been developed with invariant control on devices in the loop for a network of 100 nodes.
3
This invention can significantly enhance computational efficiency and security, leading to advances in various technology sectors and potentially lowering costs and energy consumption associated with large-scale computing.
- Computing Hardware: Enhancing performance in neuromorphic and stochastic computing
- Optimization Networks: Improving efficiency in large-scale stochastic optimization problems
- Security: Utilizing inherent noise for secure random number generation
- Neuromorphic processors and hardware
- Real-time pattern recognition and classification tasks
- Autonomous systems and robotics
- Brain-inspired computing systems
- Advanced AI research and development
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202121056949
434980