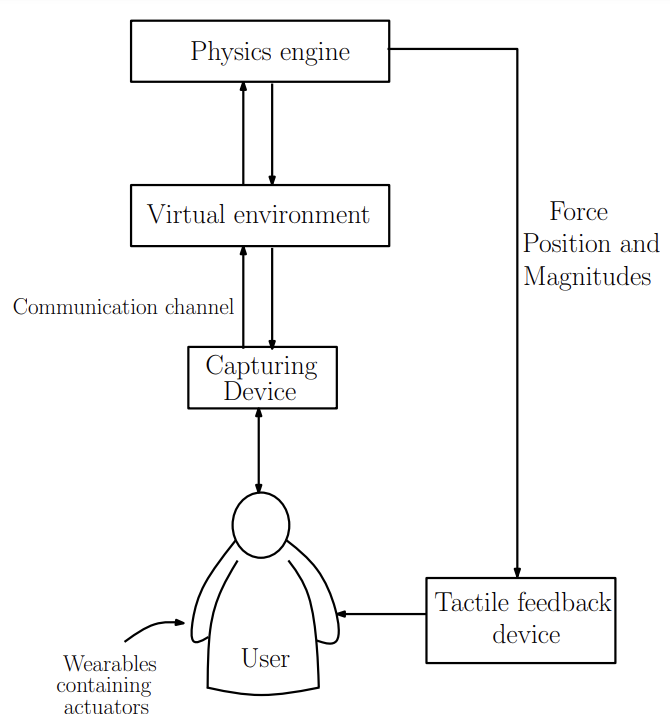
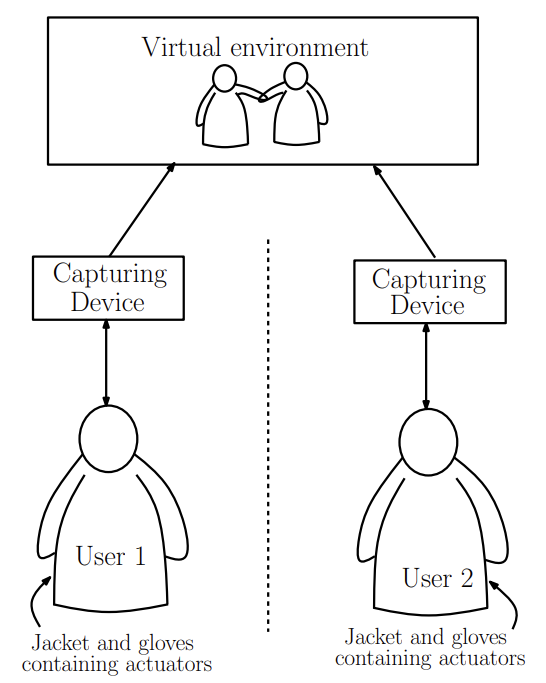
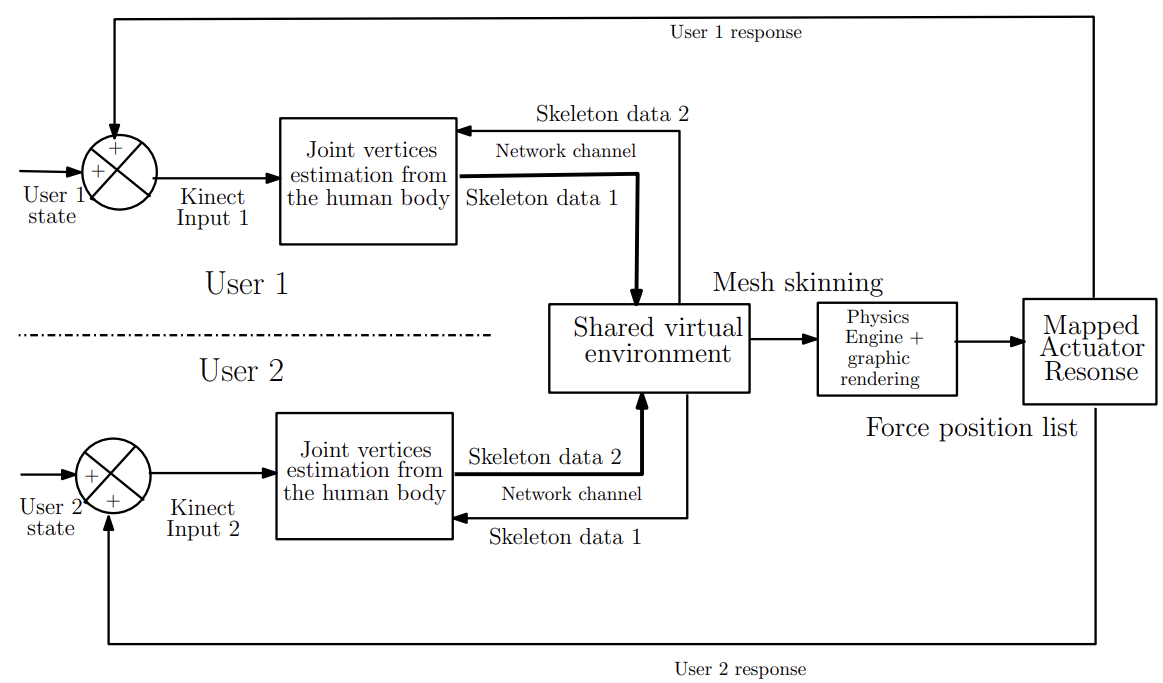
This patent introduces an advanced 3D virtual reality communication system that goes beyond typical audio and video chat by integrating tactile feedback. Using Kinect sensors, it captures users' movements to animate their virtual avatars in a shared virtual environment. This allows users to not only see and hear each other but also physically interact through touch. The system includes miniature vibrator actuators on users' clothing, which respond to collisions and interactions in the virtual world, enhancing the immersive experience. By combining these technologies, the system aims to create a more realistic and engaging communication platform suitable for multi-party interactions across different geographical locations.
The current communication systems like Zoom, WebEx, MS Teams, Skype, WhatsApp, etc. lack tactile feedback, limiting the immersive experience to audio and visual cues only. Users cannot physically interact with each other during chats, which reduces the realism and engagement of remote communication. This gap highlights the need for a telepresence system that integrates tactile perception alongside audio and visual feedback, allowing users to feel as well as see and hear each other in virtual environments. This telepresence system should enhance the sense of presence and interaction in remote communication scenarios, making conversations more realistic and engaging across distances.
- Tactile feedback integration: The innovation enables users to experience tactile sensations through miniature vibrator actuators placed as a wearable device, enhancing immersion and interaction realism in virtual environments.
- 3D avatar representation: Instead of traditional video streams, it utilizes pose estimation data to render users as interactive 3D avatars, allowing for spatial awareness and enhanced visual engagement.
- Physics-based virtual environment: The technology implements a robust physics engine to simulate real-world interactions between avatars and virtual objects, ensuring realistic collision detection and dynamic responses.
- Hierarchical body structure of the interacting body: It establishes a hierarchical bone framework based on joint positions, facilitating accurate and lifelike mesh deformation for avatar animations, enhancing visual fidelity.
- Pose estimation: It utilizes Kinect equivalent devices to precisely estimate joint coordinates, enabling real-time tracking and synchronization of user movements into the virtual environment, promoting seamless interaction.
- Real-time interaction: It supports instantaneous communication and interaction between avatars and virtual entities, enhancing user engagement and collaborative experiences in virtual spaces.
- Low hardware overhead: It optimizes system efficiency by leveraging commercially available Kinect equivalent sensors and vibrator actuators, ensuring cost-effectiveness and accessibility while maintaining high performance in virtual reality applications.
NA
This technology has reached TRL level 5. It has been implemented and demonstrated and is ready for absorption in any interactive bidirectional communication engine or platform through appropriate adaptation to the platform.
5
This innovation promotes cultural exchange and global collaboration through realistic avatar interactions and shared virtual environments. It facilitates remote learning and professional training with enhanced engagement and realistic simulation capabilities.
The technology supports therapeutic applications by enabling tactile feedback and immersive environments for rehabilitation and mental health treatments. It encourages innovation in communication technologies, potentially redefining how people interact and collaborate across distances.
Information and communications technology (ICT), Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), Bi/multi-agent communication and interaction, virtual reality, immersive environments, tactile feedback, video conferencing applications, messaging applications, haptics, physics simulation
Geography of IP
Type of IP
503/MUM/2015
430440