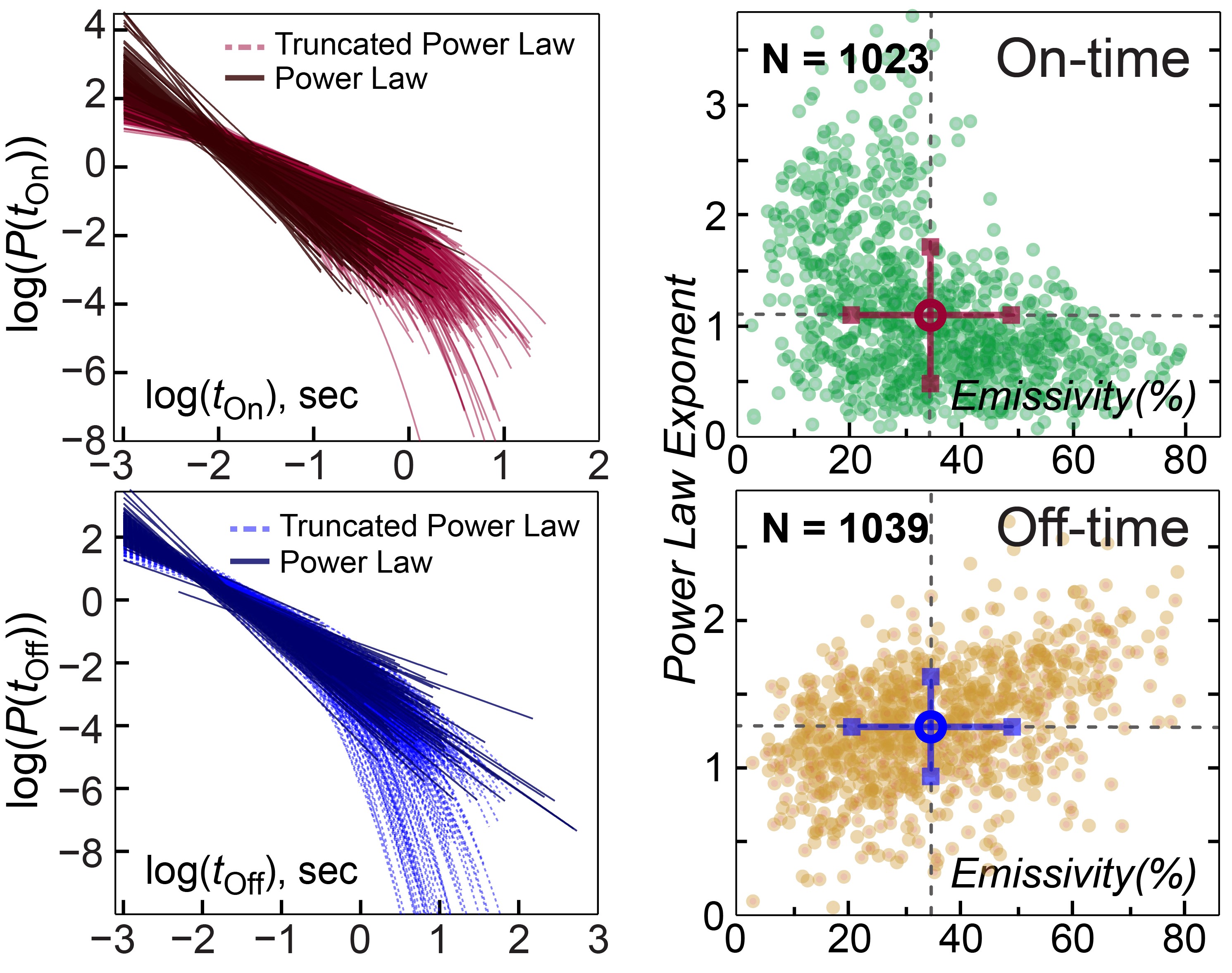
This innovative process is an automated method and system for analyzing photo-luminescence (P-L) intermittency, or "blinking," in semiconductor quantum dots (QDs). This method involves exciting single QDs, collecting image and raw blinking movies, and extracting P-L blinking trajectories from this raw data. It uses an Intensity Histogram Dependent Thresholding (IHDT) technique for grey-free two-state blinking analysis and conventional FT techniques to classify blinking characteristics. The system automates the detection and analysis processes, enabling efficient and detailed statistical analysis of QDs' blinking behaviors, which is crucial for understanding material quality and improving opto-electronic device performance.
Quantum Dots (QDs) are tiny particles with great potential for use in technologies like displays and medical imaging. However, their inconsistent light emission, known as blinking, poses a significant challenge. Traditional methods to analyze this blinking are unreliable and labor-intensive, often misclassifying light levels and requiring extensive manual work. This makes it difficult to study large numbers of QDs efficiently. We need an automated, reliable method to accurately analyze QD blinking, eliminate errors, and handle large datasets quickly, ensuring consistent and precise results.
- Automated Analysis: This technology eliminates the need for manual intervention by automating the analysis of QD blinking patterns.
- High Accuracy: It utilizes advanced algorithms to accurately classify light emission levels, reducing errors.
- Scalability: It is capable of handling large datasets efficiently, enabling the study of numerous QDs simultaneously.
- Consistency: It provides reliable and consistent results, overcoming the inconsistencies of traditional methods.
- Error Reduction: It minimizes misclassification and manual errors, ensuring more precise analysis of QD behavior.
This technology is ready for deployment.
The automated system for classifying light emission levels of quantum dots has been developed. The process has been tested and proven and is ready for deployment. Testing has shown high accuracy and reliability in classifying blinking patterns, significantly reducing misclassification and manual errors.
9
This technology greatly enhances efficiency of fluorescence microscopy data analysis that benefit medical or material imaging and interpretation. It accelerates detailed analysis of thousands of single-molecule photoluminescence data sets, benefiting researchers, companies, and universities engaged in advanced materials research and quantum optics.
- LED and QD-based Industries: High-definition displays with vibrant colors and energy efficiency
- Single Molecule Fluorescence Spectroscopy/QD-based Bio-imaging: Advanced biomedical imaging for precise disease diagnosis and treatment monitoring
- Others: QD synthesis industries, Biotechnological industries, Optical microscope companies, Microscopy industry
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202121058045
410789