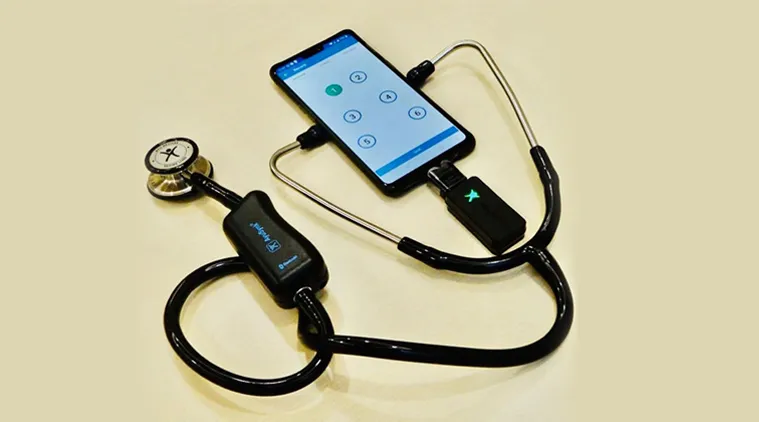
A Digital Stethoscope
This technology focuses on a connector designed for use with stethoscopes, enabling both acoustic and digital sound transmission. The connector features a modular design that allows it to be attached to a conventional stethoscope, converting it into a hybrid device capable of operating in three modes: acoustic, electronic wired, and electronic wireless. This technology addresses the limitations of conventional stethoscopes, such as restricted mobility and the need for proximity during auscultation, which can be problematic during epidemics. The connector allows acoustic and digital transmission of body sounds, enabling simultaneous hearing by multiple users and electronic recording. Key features include modular design, flexible switching between acoustic and digital modes, and wireless functionality. This innovation significantly enhances the utility of stethoscopes, making them more versatile and user-friendly in various medical scenarios.
Conventional stethoscopes, while effective for basic auscultation, lack amplification capabilities, hindering the detection of faint sounds. Existing electronic stethoscopes, although offering amplification, are often mobile-dependent, bulky, and may distort high and low-frequency sounds. Moreover, the fixed design of current stethoscopes restricts user flexibility and poses challenges during epidemics due to proximity concerns. This connector converts any acoustic stethoscope into a digital one, enabling both wired and wireless functionality without compromising the traditional design. This would provide enhanced amplification, recording, and analysis of body sounds, along with the flexibility for simultaneous auscultation by multiple users remotely.
- Hybrid Functionality: Offers both acoustic (mechanical) and digital (electronic) modes of operation for stethoscopes, switchable via a mechanism, enabling conventional auscultation and electronic sound processing.
- Signal Amplification: It features a series of progressively narrowing acoustic channels that naturally amplify sound waves as they travel towards the earpiece, enhancing audibility without electronic amplification in acoustic mode.
- Wired & Wireless Operation: The digital mode supports both wired and wireless configurations. The wired configuration allows for charging the battery and deactivates the wireless functionality to conserve power. The wireless mode enables spatial separation of the chest piece and earpiece(s).
- Split-Mode (One-to-Many) Transmission: The wireless configuration supports communication between one chest piece and multiple earpieces or external devices (computational or mobile) simultaneously, facilitating remote auscultation and collaborative diagnosis.
- Integrated Noise Cancellation: The connector incorporates active noise cancellation using an additional transducer to capture ambient noise. This noise is processed in conjunction with the sound input from the primary transducer to reduce background interference, providing a clearer audio signal, particularly beneficial in noisy environments.
- Enhanced User Experience: The connector allows recording, playback, and other control functions through integrated buttons, improving the user interface and functionality in digital mode.
The technology is a connector designed to enhance the functionality of a conventional acoustic stethoscope. It comprises two primary parts: a first piece coupled to the chest piece and a second piece coupled to the earpiece. An inner element, displaceable within the first piece, houses transducers and a switching mechanism. This mechanism, typically a knob, allows users to alternate between acoustic and electronic modes. In the acoustic mode, sound waves traverse through extruded channels in both pieces and the inner element, with a diameter reduction across channels for sound amplification. In the electronic mode, transducers convert acoustic waves into electrical signals and vice versa, enabling wired or wireless transmission. The wireless mode supports one-to-one or one-to-many communications, allowing a single chest piece to transmit data to multiple earpieces or remote devices. Locking couplers ensure secure connections between channels. While specific materials and dimensions are not explicitly stated, the channels are designed to taper along the sound direction, further enhancing sound concentration. In essence, this connector modernizes traditional stethoscopes, offering amplified acoustics, digital recording, and wireless transmission capabilities, thereby enhancing diagnostic capabilities.
By enabling the conversion of traditional acoustic stethoscopes into digital and wireless devices, the invention could bridge a critical gap in resource-limited settings, where electronic stethoscopes might be cost-prohibitive. This transformation could facilitate remote auscultation, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor patients in geographically distant locations, thereby improving healthcare access in underserved areas. Moreover, the ability to record and transmit auscultated sounds opens avenues for telemedicine consultations, second opinions, and even automated analysis using artificial intelligence, potentially leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses. This technology could also contribute to improved infection control by enabling split-mode functionality, allowing healthcare workers to maintain a safe distance from potentially contagious patients during auscultation.
Its primary application domain lies squarely within the healthcare and medical devices sector, enabling a seamless transition from traditional acoustic auscultation to sophisticated digital analysis, the core technological principles present intriguing possibilities for adaptation in other sectors.