The invention discloses a dual-charged graphene oxide (GO) filter system comprising positively and negatively charged GO papers that work in tandem to remove both cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solutions. The system demonstrates high dye removal efficiencies (≥99.9%) for common pollutants such as methylene blue and methyl orange. The filters are fabricated using a vacuum filtration method, are thermally stable up to 500°C, mechanically flexible, and can be stacked to increase adsorption capacity. The technology offers a scalable, reusable, and efficient solution for wastewater treatment applications.
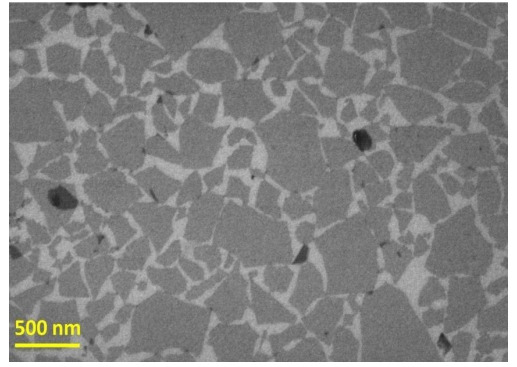
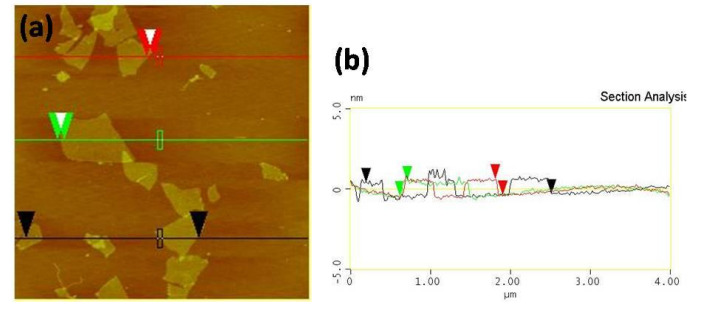
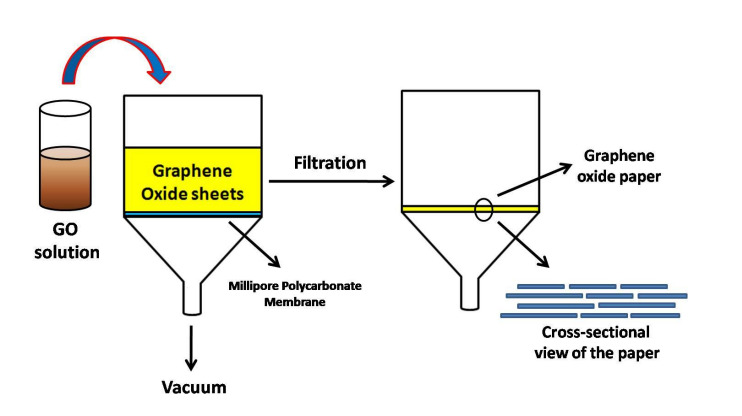
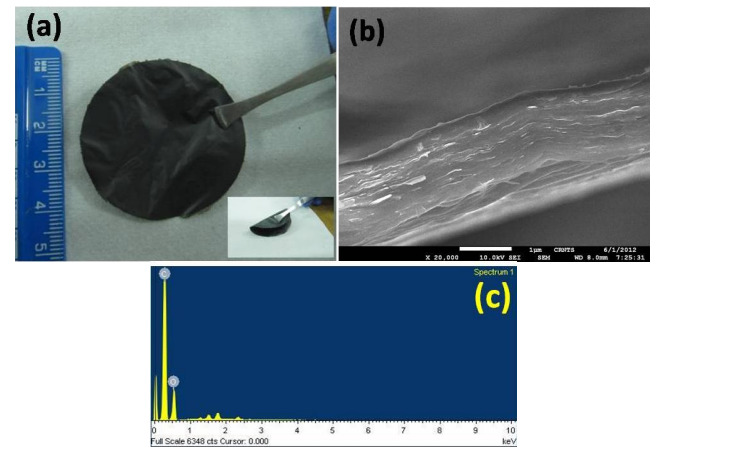
Figure (1) SEM image of monolayer of graphene oxide in Si/SiO2 substrate; (2a) AFM image of monolayer of graphene oxide, (2b) corresponding sectional analysis; (3) Schematic of the graphene oxide paper (GOPER) fabrication set-up; (4a) Photograph of the graphene oxide paper (GOPER) formed from graphene oxide solution by vacuum filtration technique. Inset shows the flexibility of the GOPER, (4b) Cross-sectional image of the GOPER, (4c) A representative EDS spectrum of the GOPER
Conventional water purification methods lack the ability to efficiently and simultaneously remove both cationic and anionic dyes from contaminated industrial effluents. Existing adsorbents typically require separate treatment steps for different dye types, involve complex fabrication processes, are often non-reusable, and lack flexibility in deployment. Furthermore, these solutions may be inefficient for mixed dye systems and are prone to secondary contamination or reduced adsorption capacity over time. Therefore, there exists a need for a cost-effective, environmentally benign, reusable filter adsorbent capable of dual dye removal in a single step with high efficiency, scalability, and mechanical stability.
- Graphene Oxide-Based Adsorption: This technology uses functionalized graphene oxide monolayers with opposite charges (GO− and GO+) for dual dye targeting.
- Layered Filter Structure: This innovation has stackable architecture, which allows control over removal efficiency based on dye concentration.
- Surface Functionalization: The positive charge introduced using polyallylamine hydrochloride (PAH) for GO+ formation.
- Vacuum Filtration Assembly: It is fabricated via a low-cost, scalable vacuum assembly using polymeric membranes.
- Mechanical Durability: This technology demonstrates uniform mechanical strength and elasticity through nanoindentation analysis.
- Thermal Robustness: It is stable up to ~500°C as confirmed via thermogravimetric analysis.
The prototype consists of a dual-layer filter system composed of positively charged and negatively charged graphene oxide (GO) papers. These GO papers were fabricated using a vacuum filtration process on a microporous cellulose nitrate membrane. The positive GO paper was prepared by modifying GO with polyethyleneimine (PEI), while the negative GO paper was derived from unmodified GO dispersion. The filter stack was assembled by layering the charged GO papers to form a cohesive dual-charged structure. The assembled prototype was tested for removal of methylene blue and methyl orange dyes, demonstrating >99.9% removal efficiency. The system also showed stability across multiple adsorption-desorption cycles and retained mechanical integrity under testing conditions.
The technology has been demonstrated at a laboratory scale using a vacuum filtration-based fabrication method. Dual-charged graphene oxide filters have been successfully synthesized and tested for high-efficiency dye removal, achieving >99.9% removal of both methylene blue and methyl orange dyes. Reusability and structural integrity have been validated through multiple adsorption-desorption cycles under ambient conditions. The process is scalable and uses readily available materials, showing strong potential for upscaling. However, pilot-scale deployment and industrial field trials are yet to be initiated.
4
The dual-charged graphene oxide-based filter adsorbent offers an efficient and scalable solution for treating dye-laden industrial wastewater, which is a major source of environmental pollution. By simultaneously removing both anionic and cationic dyes with over 99% efficiency, the technology significantly reduces toxic dye discharge into freshwater sources, thereby protecting aquatic ecosystems and public health. The use of cost-effective, reusable, and environmentally friendly materials makes the solution accessible for widespread adoption, especially in resource-limited industrial settings. Moreover, the modular design promotes sustainability by enabling regeneration and long-term use, contributing to cleaner water management and improved environmental standards.
- Textile and dyeing industries: Effective for treating dye-contaminated effluents before discharge
- Industrial wastewater treatment plants: Applicable for removal of cationic and anionic pollutants in large-scale operations
- Environmental remediation: Suitable for controlling dye pollution in contaminated surface water and groundwater
- Modular filtration systems: Can be integrated into stacked or layered filter cartridges for scalable purification setups
- Water purification product manufacturers: Useful in developing cost-effective and efficient filtration units for industrial or decentralized applications
Geography of IP
Type of IP
1626/MUM/2015
367378