The invention discloses the methods for eliminating the delamination (layering) defects during the mechanical drilling of the fiber-reinforced composite material part. There are the following methods proposed in this invention to avoid delamination (Peel-up and Push-out) damages.
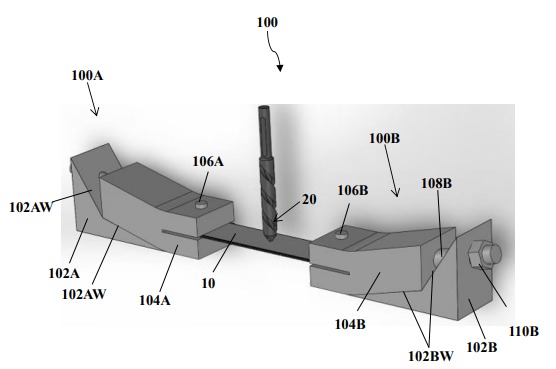
(i) Drill from both sides, which avoids the formation of push-out delamination damages.
(ii) Create z-pinning stitches around the site where the hole has to be created. This could be a circumferential inside and radial outside to avoid both peel-up and push-out delamination.
(iii) The peel-up (pull-out) damage can be reduced by having a varying pitch of the Helix of the drill bit. And the pitch slightly above the tooltip should decrease to a very low value reducing peel-up damage.
These methods have the advantage of effectively eliminating the layering damages, the use is convenient, and therefore, there are many potential engineering applications.
Fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) composite components are difficult to drill due to their non-uniformity, anisotropy, and abrasiveness. Drilling induces defects such as fiber pull-out, matrix fracturing, and delamination, especially push-out delamination at the hole exit, caused by thrust force exceeding interlayer bonding strength. This results in structural integrity loss and reduced mechanical properties. Conventional methods like rear surface metal plates, tape, and controlled low-temperature drilling are costly and ineffective, particularly against push-out delamination. These methods require sophisticated apparatus and increase production costs. Therefore, a need exists for a system and method to reduce drilling induced defects in FRP composites.
- Delamination Prevention: Proposed methods effectively prevent delamination damage (push-out/pull-out) and are convenient to use.
- Balanced Support during Drilling: As the drilling force varies, maximum at the center to the circumference of the drill tool, both sides of drilling provide the backup support force to counter the drill penetration.
- Double Sided Drilling: Drilling from both sides minimizes mode II (sliding shear) failure by supporting plies.
- Critical Thrust Force: Proposed Methods increase critical thrust force, enabling higher feed rates of the drilling and productivity.
- Z-pinning: Z-pinning stitches around the hole reduce circumferential damage as it provides bonding support.
- Variable Helix Pitch: Varying the pitch of the helix of the drill bit reduces the peel-up (pull-out), which provides a good quality product and increases productivity.
- Combined Method Approach: Proposed Methods can be combined for high-quality FRP drilling.
NA
The technology is demonstrated in controlled environment drilling experiments in the lab, which is similar to industrial machining.
4
This process lowers manufacturing costs of high-performance composites. It minimizes material waste and reduces rework thus promoting sustainability. Moreover, it enhances the structural integrity of parts used in aerospace, automotive, and defense sectors, reducing risk of failures.
- Aerospace industry
- Automotive industry
- Wind energy sector
- Defense and Military
- Material science
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202321054686
560883