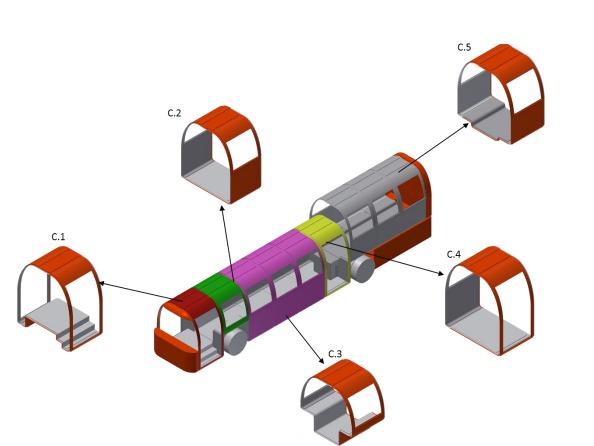
This invention describes a vehicle body, particularly for buses, made from a layered structure consisting of an inner and outer cover with a middle core for support. In the first method, the core is made from foamed materials like aluminum foam, foamed plastic, or foamed ceramic, which are placed between two metal layers. In the second method, a chemical process called Reaction Injection Molding is used to create the sandwich structure, where the middle layer becomes part of the inner and outer layers. The vehicle body is built from individual modules, each with its own sandwich structure, and these modules are easily joined together using flanges on the layers that fit together for quick and simple assembly.
The conventional process for manufacturing vehicle bodies, particularly buses, relies heavily on complex metallic structures that require welding, which is labor-intensive, environmentally harmful, and results in a heavy vehicle. The production process also involves toxic chemical products, leading to high environmental impact, poor worker health, and increased manufacturing costs. Moreover, these heavy buses negatively affect fuel consumption, contribute to higher road wear, and increase maintenance costs. There is a need for a more efficient, lightweight, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional vehicle body construction.
- Modular Body Structure: The vehicle body is constructed using a series of interconnected body modules, each comprising a sandwich structure with an outer cover layer, inner cover layer, and an intermediate core.
- Integrated Features: The body modules include integrated components such as seats, service ducts, and windows, reducing the complexity and number of parts needed for assembly.
- No Welding Required: The modular panels are joined without welding, using lap joints, rivets, clips, or adhesives, eliminating the need for welding and sanding, and minimizing toxic emissions.
- Lightweight and Rigid Design: The sandwich structure, which combines lightweight materials like foam or honeycomb cores with durable cover layers, provides the required strength and rigidity while minimizing the overall vehicle weight.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: The use of materials like stamped aluminum, foamed metals, or composite plastics, along with non-toxic processes, reduces the environmental impact and worker exposure to harmful substances.
- Reduction in Manufacturing Costs: By simplifying the assembly process, reducing parts, and eliminating welding and sanding steps, the technology reduces overall manufacturing time and cost.
- Enhanced Fuel Efficiency: The reduction in vehicle weight directly contributes to improved fuel economy, leading to lower fuel consumption and emissions during vehicle operation.
The prototype of this modular vehicle body consists of body modules formed using sandwich panels, which are made of two outer cover layers (typically stamped aluminum or plastic) with an intermediate core of foam or honeycomb material. The modules are pre-assembled with integrated features like windows, seating arrangements, and service ducts. These modules are connected using lap joints or other fitting techniques, ensuring that the assembly is quick and requires minimal tooling. The body design is scalable, and the modular system can be adapted for different vehicle sizes and applications.
The technology is at concept development stage.
2
The societal impact of this technology is significant, with environmental benefits such as reduced fuel consumption and lower carbon emissions. The elimination of welding and sanding processes improves worker health by reducing exposure to harmful fumes. Economically, the simplified production process lowers costs, leading to more affordable vehicles and higher adoption rates. Additionally, the reduction in vehicle weight saves energy, contributing to national fuel savings and reducing dependence on imported petroleum products.
- Automotive Industry: It is particularly useful in the design and production of buses, trains, and other mass transit vehicles, where weight reduction and efficiency are crucial.
- Public Transport: The technology can revolutionize the way city buses and mass transit systems are constructed, offering more energy-efficient and cost-effective vehicles.
- Manufacturing: The modular approach can be adapted for various types of vehicles or mobile structures, including commercial trucks, vans, and even mobile infrastructure.
- Sustainability and Green Technologies: The technology's focus on reducing environmental impact through lightweight and sustainable materials makes it relevant in industries striving for greener solutions.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
2290/MUM/2015
381997