The present invention discloses self-assembled, multi-fluorescent carbon nanostructures, particularly graphene quantum dots (sGQDs), designed for selective labeling of the cytoplasm and nucleus, as well as various biomedical applications such as pH sensing, wound healing, and temperature sensing. These sGQDs are synthesized using a green, cost-effective method with grape seed extract as a natural, biocompatible carbon source. The synthesis process is simple, rapid, and does not require multiple purification steps. The resulting sGQDs exhibit excellent fluorescence properties and inherent biocompatibility, making them ideal for diagnostic and therapeutic use.
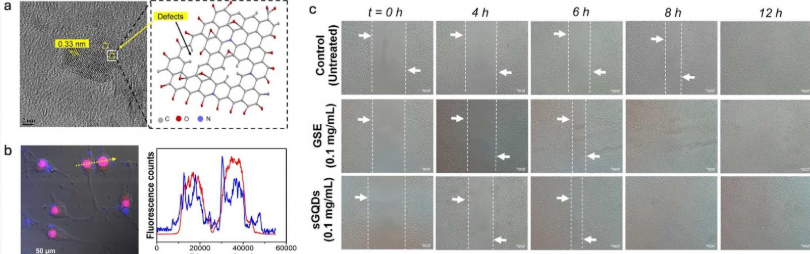
Figure 1. (a) An FEG-TEM micrograph showing lattice fringes with lattice spacing of 0.33 nm which corresponds to (006) diffraction plane of graphitic carbon (JCPDS 26–1076); (b) CLSM images are showing cellular intake and localization of sGQDs in the nuclei of L929 cells. Merged image of all channels (left) showing the differential Interference Contrast image, DAPI (blue) localization in the nuclei along with the Red laser excitation showing localization of the sGQDs from the cell cytoplasm to the nucleus; (c) A representative microscopic images showing in vitro cell proliferation-inducing property of sGQDs in L929 cells (Scale bar: 100 µm) with GSE as control; Publication: Kumawat, Mukesh Kumar, et al. "Graphene quantum dots for cell proliferation, nucleus imaging, and photoluminescent sensing applications." Scientific reports 7.1 (2017): 15858.
Conventional methods for synthesizing graphene quantum dots (GQDs) often rely on hazardous or inconsistent natural carbon sources, require complex purification steps, and yield products with limited biological specificity. Additionally, many GQDs fail to efficiently stain the nucleus or exhibit therapeutic benefits. There is a need for a simple, safe, and green synthesis method using a consistent and biocompatible carbon source to produce multifunctional GQDs with enhanced imaging and therapeutic properties.
- Green and Cost-Effective One-Pot Synthesis: The invention uses a simple, eco-friendly microwave-assisted method with grape seed extract as a carbon source, avoiding toxic reagents and reducing synthesis time and cost.
- High Biocompatibility and Low Toxicity: The sGQDs exhibit excellent biocompatibility, confirmed through >95% cell viability in L929 fibroblast cells, making them safe for in vitro biomedical applications.
- Selective Nucleus Labeling and Self-Localization: sGQDs show selective nucleus labeling and self-localization inside the nucleus without any tagging agent, as demonstrated by CLSM imaging.
- Multi-Fluorescent and Photostable Behavior: The sGQDs are multi-fluorescent, stable under different pH conditions, and photostable over time, suitable for bioimaging applications.
- Proven Wound Healing and Proliferative Activity: sGQDs promote cell proliferation and demonstrate wound healing ability in vitro, expanding their application beyond diagnostics into therapeutics.
The process of synthesis of the sGQDs is described below:
The synthesis process of self-assembled graphene quantum dots (sGQDs) begins by dissolving grape seed extract (GSE) in an alcoholic solvent at room temperature for at least 5 minutes. The resulting solution is then centrifuged, and the supernatant is collected. The solvent from the supernatant is evaporated under vacuum using a rotary evaporator at a temperature of about 50°C–60°C to obtain a dry solid. This solid is then dispersed in an aqueous medium and subjected to microwave heating at approximately 150°C–180°C for about 2–5 minutes, resulting in the formation of graphene quantum dots. Optionally, the product may be further purified by re-dispersing the obtained solid in an alcoholic solvent. The final sGQDs produced range in size depending on the solvent used – approximately 1–8 nm in alcoholic medium and 30–90 nm in aqueous medium.
Technology synthesized and evaluated in vitro in proof-of-concept.
3
This invention provides a sustainable and cost-effective approach to synthesizing graphene quantum dots using grape seed extract, a natural and readily available material. By avoiding toxic chemicals and complex procedures, it promotes safer nanomaterial production. The biocompatible and multifunctional sGQDs enable advanced biomedical applications such as targeted imaging, pH sensing, and wound healing. Overall, it supports the development of eco-friendly, affordable nanotechnologies with direct benefits to healthcare and diagnostics.
- Biomedical imaging and diagnostics
- Nanomaterials and nanotechnology
- Drug delivery and therapeutic systems
- Regenerative medicine and wound care
- Green chemistry and sustainable materials
- Biotechnology and life sciences research
- Clinical diagnostics and cellular imaging
- Functional nanomaterials for healthcare
Geography of IP
Type of IP
201621011794
470668