The present invention relates to a composite drug delivery system comprising drug loaded polymeric microparticles embedded within the hydrogel matrix. The present invention also relates to the process for preparing the afore-mentioned composite drug delivery system. The present invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions or injectable formulations for sustained release of drugs comprising the afore-mentioned composite drug delivery system.
There is a critical need for improved local drug delivery systems that offer long residence time at the target site and controlled drug release to reduce frequent injections. Existing particulate and hydrogel-based systems face limitations in injectability, stability, and sustained release. To overcome these challenges, the invention presents a composite system of drug-loaded polymeric microparticles embedded within a biocompatible hydrogel matrix for enhanced localized therapy.
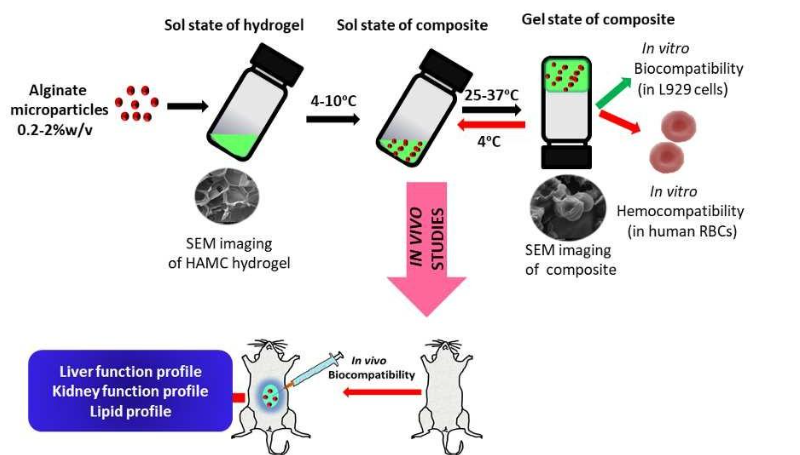
- Composite Structure: The process yields drug-loaded polymeric microparticles embedded within a shear-thinning, thermoresponsive hydrogel matrix (sodium hyaluronate and methylcellulose).
- Injectability: It is easily injectable through clinically relevant needle gauges (26G, 24G, 18G) at room temperature without extra force.
- Thermoresponsive Gelation: It is liquid at room temperature and forms a semi-solid gel rapidly (~5 minutes) at body temperature (37°C) for localized retention.
- Dual-Barrier Controlled Drug Release: Microparticles inside the hydrogel create a dual barrier, significantly slowing and sustaining drug release.
- Rheological Stability and Shear-Thinning Behaviour: It has viscoelastic properties with shear-thinning ensure smooth injection and gel formation.
- Sterilizable and Stable: It maintains gelation, morphology, and thermal reversibility after sterilization and long-term frozen storage.
The present invention provides a process for preparing a composite drug delivery system comprising drug-loaded polymeric microparticles embedded within a hydrogel matrix. First, the drug-loaded microparticles are prepared using methods such as water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion solvent diffusion, where the drug is encapsulated within polymers like alginate. Separately, a hydrogel matrix is prepared by physically blending polymers selected from sodium hyaluronate, methylcellulose, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, xanthan gum, poloxamer, or combinations thereof. The polymer concentrations are optimized to achieve desired properties such as gelation time, injectability, and thermal responsiveness. Once both components are ready, the drug-loaded microparticles are dispersed into the viscous hydrogel matrix at a low temperature range of 4°C to 10°C. This results in a homogeneous composite formulation, where the microparticles are uniformly embedded within the hydrogel network. The final product is a thermoresponsive, injectable system suitable for localized and controlled drug delivery.
This patent includes formulation development, physicochemical characterizations, and completed preclinical trials, now seeking financial support to refine and scale up the formulations for further clinical trials.
These technologies are available for licensing to industry partners or collaboration for further development.
4
The composite drug delivery system offers improved localized treatment by reducing injection frequency through sustained drug release, enhancing patient comfort and compliance. Its injectable and biocompatible nature supports minimally invasive therapy, potentially lowering healthcare costs and hospital visits. By enabling more effective and controlled drug delivery, it can improve treatment outcomes for chronic diseases, benefiting patients and healthcare systems alike.
- Pharmaceuticals
- Biotechnology
- Healthcare and Medical Devices
- Cosmeceuticals
- Veterinary medicine
- Polymer formulations
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202021055157
433347