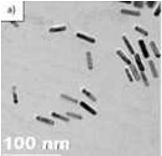
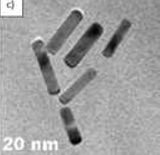
The present invention provides a reproducible and scalable method for synthesizing Au-Pt bimetallic nanorods using dodecyl ethyl dimethyl ammonium bromide (DMAB) as a biocompatible growth-directing agent. The method eliminates the need for freshly prepared seed solutions and overcomes limitations related to poor stability and cytotoxicity observed with conventional CTAB-based approaches. The resulting nanorods exhibit excellent long-term stability in growth solution for up to one month at room temperature, making them highly suitable for biomedical and photothermal applications.
Conventional seed-mediated synthesis of gold nanorods faces challenges like low yield, poor uniformity, and the need to freshly prepare unstable seed solutions each time. The process is highly sensitive to slight changes in reactants, pH, and temperature, leading to poor reproducibility. Additionally, CTAB, the common surfactant, is cytotoxic and unsuitable for biomedical use. These limitations hinder consistent experimentation and raise production costs. There is a need for a stable, reproducible, and biocompatible method to synthesize tunable bimetallic nanorods.
- Reproducible and Scalable Synthesis: The process enables consistent production of Pt-Au bimetallic nanorods with controllable aspect ratios, enhancing batch-to-batch uniformity.
- Enhanced Stability: Synthesized nanorods exhibit long-term stability (up to one month) in growth solution at room temperature, reducing waste and preparation time for repeated experiments.
- Controlled Aspect Ratio and LSPR Tuning: Each reactant in the synthesis affects the nanorod's aspect ratio, allowing precise tuning of the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) peak for specific biomedical and photothermal applications.
- Cost-Effective and Efficient: It eliminates the need for freshly prepared seed solutions and complex handling lowering operational costs and increasing synthesis efficiency. It also offers reduced cytotoxicity compared to conventional CTAB-based methods.
The process for preparing Pt-Au bimetallic nanorods begins with the preparation of a seed solution containing gold nanoparticles using the quaternary ammonium surfactant, Dodecyl Ethyl Dimethyl Ammonium Bromide (DMAB). In the next step, silver nitrate is added to a chloroauric acid (HAuCl₄) solution in the presence of DMAB, which serves as a growth-directing agent. To this mixture, potassium tetrachloroplatinate and ascorbic acid are added, followed by stirring for 5–10 minutes to allow the reduction of metal ions and initiate the formation of bimetallic structures. Subsequently, the gold seed solution is introduced into the reaction mixture and stirred for 10–15 minutes until the solution turns dark pink, indicating the successful formation of Pt-Au bimetallic nanorods.
Technology has been synthesized and evaluated in vitro; it has not yet been evaluated beyond proof-of-concept.
3
The invention facilitates the development of advanced, less toxic nanomaterials for cancer diagnostics and photothermal therapy, enhancing treatment specificity and reducing side effects. It enables cost-effective, stable nanorod production, promoting broader accessibility to nanomedicine. Additionally, the method supports safer alternatives to cytotoxic surfactants, contributing to improved public health outcomes.
- Biomedical and Healthcare
- Nanotechnology
- Pharmaceutical
- Diagnostic imaging
- Cancer research and therapy
- Materials science and engineering
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202021042970
414280