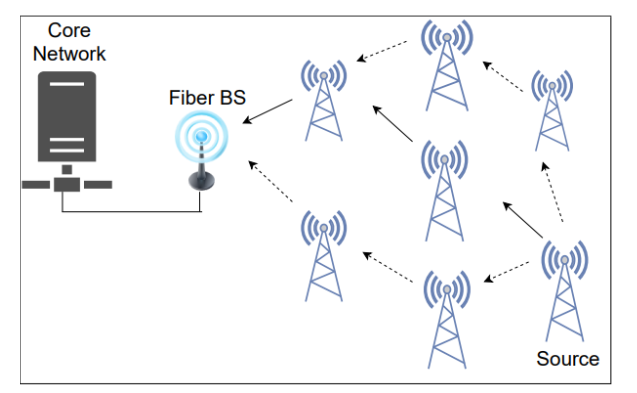
This invention provides a method for scheduling self-backhaul links in millimeter wave (mmWave) networks with low latency. The method considers the queue lengths at each base station (BS) and the distances to the fibre-BS to determine which links should be activated in each time slot. By optimizing the scheduling based on these factors, the invention ensures a low average delay in sending packets from self-backhauled BS (S-BSs) to the fiber-based BS (fibre-BS), thereby improving the overall performance and efficiency of mmWave self-backhaul networks.
Millimeter wave (mmWave) networks, while offering high bandwidth, face significant challenges due to high path loss and low propagation across barriers, leading to coverage limitations. To address these issues, Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) has introduced self-backhaul techniques to enable dense network deployment at a lower cost. However, current self-backhaul methods do not consider packet queue lengths at self-backhauled BS (S-BSs), leading to suboptimal performance and high average delay in packet transmission. This invention addresses these shortcomings by proposing a method that schedules self-backhaul links with low latency, considering the queue lengths at each S-BS, thereby optimizing the transmission of packets from S-BSs to a fiber-based BS (fibre-BS).
- Queue Length Consideration: The scheduling method takes into account the queue length at each S-BS, ensuring that packets are transmitted efficiently.
- Distance-Based Link Activation: Links are activated based on the distance from the S-BS to the fibre-BS, ensuring that the link with the shortest path is prioritized.
- Dynamic Link Scheduling: The method dynamically schedules links in each time slot to minimize average delay and optimize packet transmission.
- Scalability: The method is scalable and can be applied to networks with varying numbers of S-BSs and fibre-BSs.
The prototype consists of a mmWave network with at least one fibre-BS and multiple S-BSs. Each S-BS has a scheduling module, a communication module, and a memory module. The scheduling module calculates the queue length and the distances to the fibre-BS, assigns weights to the links based on these factors, and activates the links accordingly. The communication module enables the transmission of packets over the activated links, and the memory module stores the necessary data for scheduling and transmission.
Testing and evaluation of basic concept is under process for the final objective.
3
This invention improves the performance and efficiency of mmWave self-backhaul networks, reducing latency and enhancing the overall user experience. It supports the deployment of high-speed, low-latency networks, which are crucial for applications such as 5G and beyond, enabling faster data transmission and improved service quality.
- Wireless Communication Networks: Enhances the performance of mmWave networks by reducing latency and improving packet transmission efficiency
- 5G and Beyond: Supports the deployment of 5G and future wireless communication standards
- Edge Computing: Improves the efficiency of edge computing by reducing latency in data transmission
- Telecommunications: Enhances the performance of telecommunications networks, particularly in areas with challenging propagation environments
- Data Centers: Supports the efficient transmission of data in data centers, improving overall network performance
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202321060322
559813