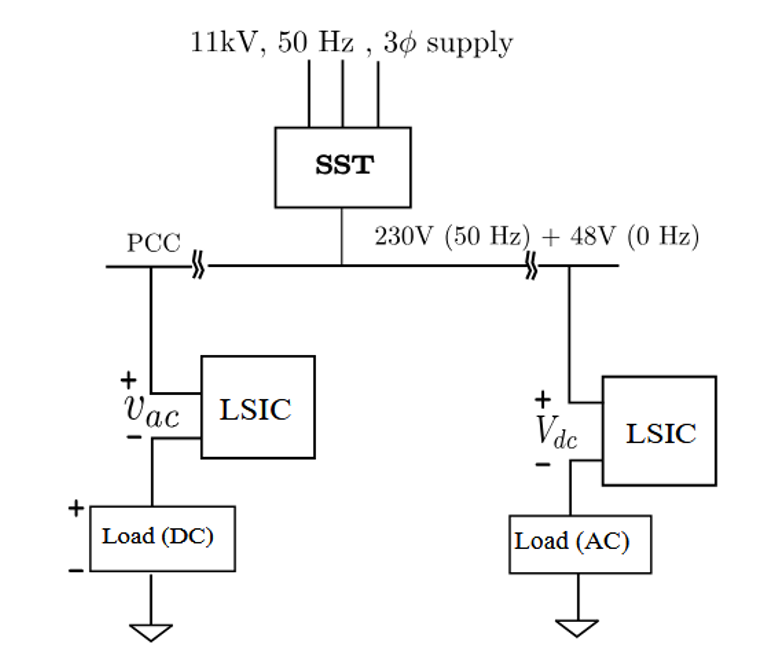
An AC-DC microgrid brings together both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) power on a single network. A special transformer feeds a mix of regular house/business electricity (230 V AC) and a low-voltage DC line (48 V). At each device or appliance, a smart converter picks off exactly the type of power needed – no extra adapters, fewer energy losses. Tests show stable operation under changing loads, making the system ready for small-scale pilots.
Traditional power systems mainly use AC (Alternating Current) electricity, even though many modern devices and renewable sources work better with DC (Direct Current). Converting between AC and DC repeatedly causes energy loss, higher costs, and adds complexity. Cities also face challenges in switching entirely to DC systems due to infrastructure constraints. There's a need for a smart, efficient system that can handle both AC and DC power smoothly for homes and industries.
- Unified AC-DC Distribution: This design carries both 230 V AC and 48 V DC on a single feeder, eliminating the need for separate wiring or bulky adapters. By delivering the exact mix of current your devices need without extra conversion steps, it cuts energy losses by up to 15% and lowers electricity bills.
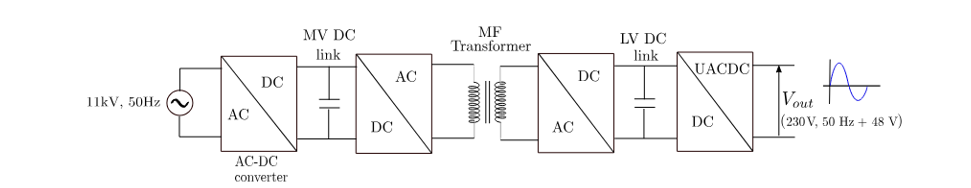
- Smart Solid-State Transformer: This technology employs a three-stage power converter with a medium-frequency isolation transformer to feed combined AC and DC at the point of common coupling.
- Load-Side Converters: This feature outfits each appliance or socket with a small series H-bridge module that automatically “picks off” either AC or DC as required. The converter fits in line with minimal size, switches seamlessly between modes, and keeps conversion losses under 2%.
- Simple Control Algorithms: This technology uses fast PI controllers and hysteresis comparators to monitor voltage and current in real time.
- Integrates Renewable Sources Easily: This design lets solar panels, wind turbines, or battery banks plug directly into the 48 V DC link without extra inverters.
A lab prototype includes a three-stage high-voltage converter, a medium-frequency transformer, and a 400 V DC link. On the low-voltage side, compact single-phase H-bridge modules connect to test loads (motors, lights, chargers). Waveforms captured on oscilloscopes verify correct AC/DC separation and rapid response to load changes.
The system has been demonstrated in a controlled setup with step-load tests for both AC and DC devices. Simulation and hardware tests confirm stable voltage and current waveforms.
5
By slashing conversion losses, households and businesses save on electricity bills. Cleaner integration of solar and batteries reduces fossil-fuel dependence and carbon emissions. Simplified wiring and fewer adapters make modern energy solutions more affordable and reliable, supporting greener, smarter communities.
- Smart homes and buildings
- Solar and battery energy systems
- Light industrial facilities
- Electric vehicle charging stations
- Data centres and telecom sites
- Off-grid or microgrid deployments
Geography of IP
Type of IP
201721001886
474593