The invention relates to the design and synthesis of urea-based hydrogen-bonding templates for meta-C–H olefination of electron-deficient arenes such as nitrobenzenes and aromatic carbonyls. These templates enable non-covalent interaction with substrates and coordination with metal catalysts to direct selective distal C–H functionalization. The process offers an atom-economical and efficient method for remote olefination without the need for covalent directing groups, making it suitable for functionalizing pharmaceutically and agrochemically relevant molecules.
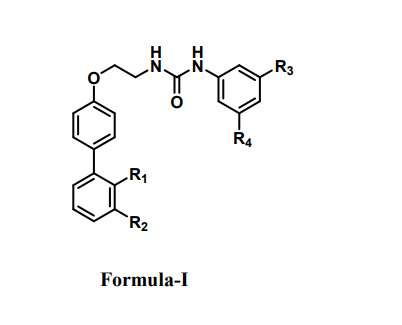
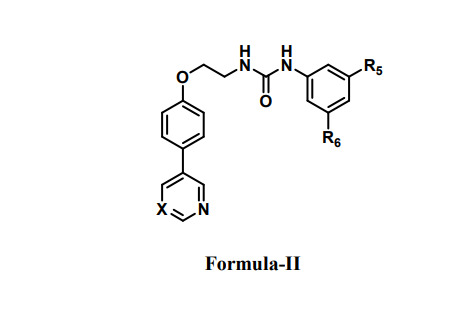
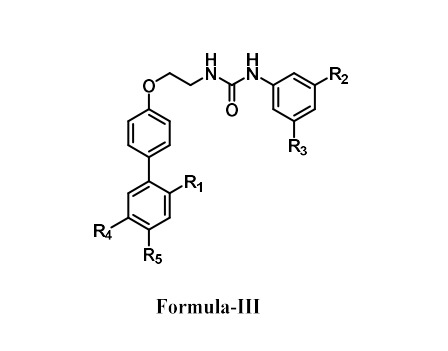
Formula (I) In the manifestation of this invention, R1 is nitrile group (-CN) when R2 is hydrogen R2 is nitrile group (-CN) when R1 is hydrogen R3 and R4 is trifluoromethyl group (-CF3); (II) In the manifestation of this invention, X is carbon or nitrogen R5 and R6 is trifluoromethyl group (-CF3); (III) In the manifestation of this invention, R1 is nitrile group (-CN) R2 and R3 is trifluoromethyl group (-CF3). R4 and R5 is methoxy group (-OMe).
Achieving selective meta-C–H olefination of electron-deficient arenes, such as nitrobenzenes and aromatic carbonyls, is highly challenging due to their low reactivity and the preferential activation of proximal C–H bonds. Existing covalent directing group methods require additional steps, reducing atom and step economy. A non-covalent, hydrogen-bond-driven strategy is needed to enable efficient and regioselective distal C–H functionalization.
- Hydrogen-Bonding Template Design: The technology introduces urea-based hydrogen-bonding templates that enable selective meta-C–H olefination of electron-deficient arenes and aromatic carbonyl compounds.
- Dual Functional Interaction: The designed templates interact with substrates through non-covalent hydrogen bonding and simultaneously coordinate with palladium catalysts to direct distal C–H activation.
- Non-Covalent Directing Strategy: The invention eliminates the need for covalent directing groups, thereby improving atom and step economy by avoiding additional installation and removal steps.
- Substrate Versatility: The templates are compatible with a wide range of functional groups, including nitro, ester, amide, ketone, and aldehyde moieties, making the method broadly applicable.
- Applicability to Functional Molecules: The technology enables late-stage functionalization of structurally complex and pharmaceutically relevant molecules, offering synthetic value in drug and agrochemical development.
- Reaction Conditions: The process achieves high meta-selectivity under mild conditions using palladium catalysts in a highly polar protic solvent such as hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP).
- Ligand-Assisted Yield Enhancement: The use of mono-protected amino acid (MPAA) ligands improves reaction efficiency and yield by facilitating effective coordination and catalytic turnover.
The prototype involves the synthesis of urea-based hydrogen-bonding templates derived from substituted biphenyl precursors and trifluoromethyl isocyanate. These templates were successfully used in palladium-catalyzed meta-C–H olefination of nitroarenes and aromatic carbonyl compounds in the presence of mono-protected amino acid ligands and polar protic solvents such as HFIP. The resulting olefinated products were purified and characterized using NMR and HRMS techniques, confirming selective meta-functionalization.
The technology has been validated at the laboratory scale with successful synthesis of urea-based hydrogen-bonding templates and their application in meta-C–H olefination of nitroarenes and aromatic carbonyl compounds. Multiple derivatives have been synthesized, purified, and characterized using NMR and HRMS techniques, demonstrating consistent regioselectivity and efficiency under optimized reaction conditions.
5
The technology enables selective functionalization of electron-deficient arenes, which are core structures in many pharmaceuticals, natural products, and agrochemicals. By offering a more efficient, atom-economical, and step-reducing approach, the invention supports greener synthesis pathways and facilitates the development of advanced molecules with potential applications in medicine and agriculture.
- Pharmaceuticals
- Agrochemicals
- Fine chemicals
- Research and development labs
- Organic synthesis service providers
- Green chemistry and sustainability
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202321079920
560190