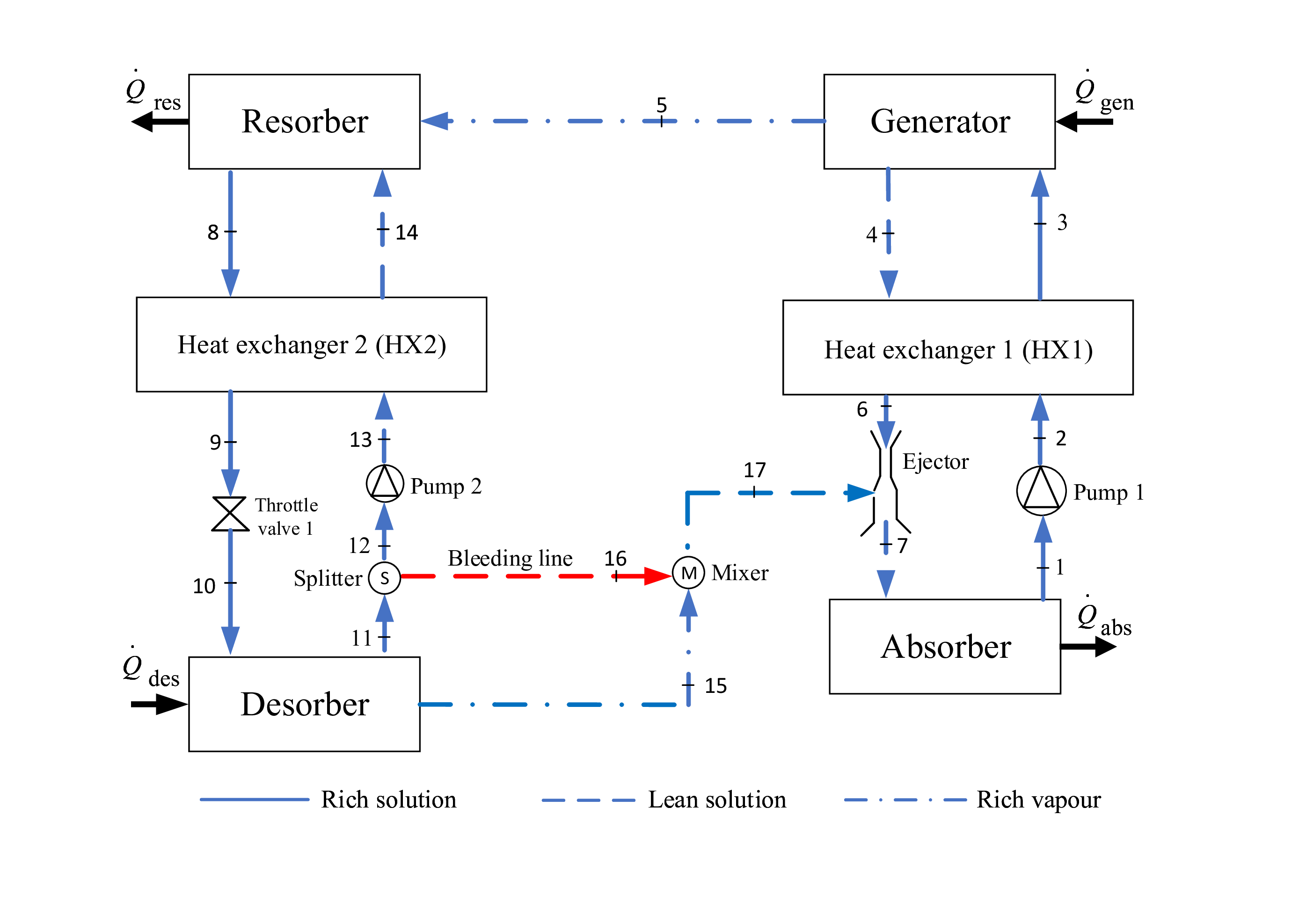
The ejector assisted absorption-resorption cycle for cooling applications presents an innovative solution to enhance the efficiency of heat-driven cooling systems. By integrating an ejector into the absorption circuit, the proposed configuration optimizes performance, reduces initial costs, and minimizes the system size compared to conventional Vapor Absorption Cooling Systems (VACS).
Cooling is essential in modern life, consuming 17% of the world's generated electricity. Traditional vapour compression systems are energy-intensive, with the mechanical compressor alone consuming about 70% of the input electricity. This results in higher CO2, especially from coal-based electricity generation. There is a need for more efficient, low-cost, heat-driven cooling technologies to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
- This technology utilizes a zeotropic mixture as the refrigerant for enhanced flexibility in operating pressures and temperatures.
- It integrates an ejector in the absorption circuit to improve efficiency by replacing certain components like expansion valves.
- It achieves Coefficient Of Performance (COP) equal to conventional Vapour Absorption Cooling Systems (VACS) at 45% lower pressure ratio.
- It provides higher COP at higher compression ratios than conventional VACS.
- It operates at lower pressure ratios without performance trade-offs, reducing initial cost and system size.
The system configurations were simulated and validated, with results compared to the state-of-the-art literature in experimental and simulation studies. The prototype has not been fabricated and tested because most of the components are off-the-shelf, and the scale of testing requires industrial support and funding.
The proposed ejector assisted Vapour Absorption-Resorption Cycle (VARC) configuration is in the research and development phase. Initial simulations and theoretical analyses have demonstrated promising results, indicating potential for higher efficiency and lower costs compared to conventional systems.
3
The adoption of this technology can significantly reduce energy consumption and CO2 emissions associated with cooling systems. It offers a sustainable solution for cooling needs, contributing to environmental conservation and energy efficiency.
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) industry:
- Industrial cooling processes
- Commercial refrigeration - food and beverage (refrigeration), pharmaceuticals (temperature-controlled storage)
- Renewable energy-driven cooling systems
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202121009303
421288