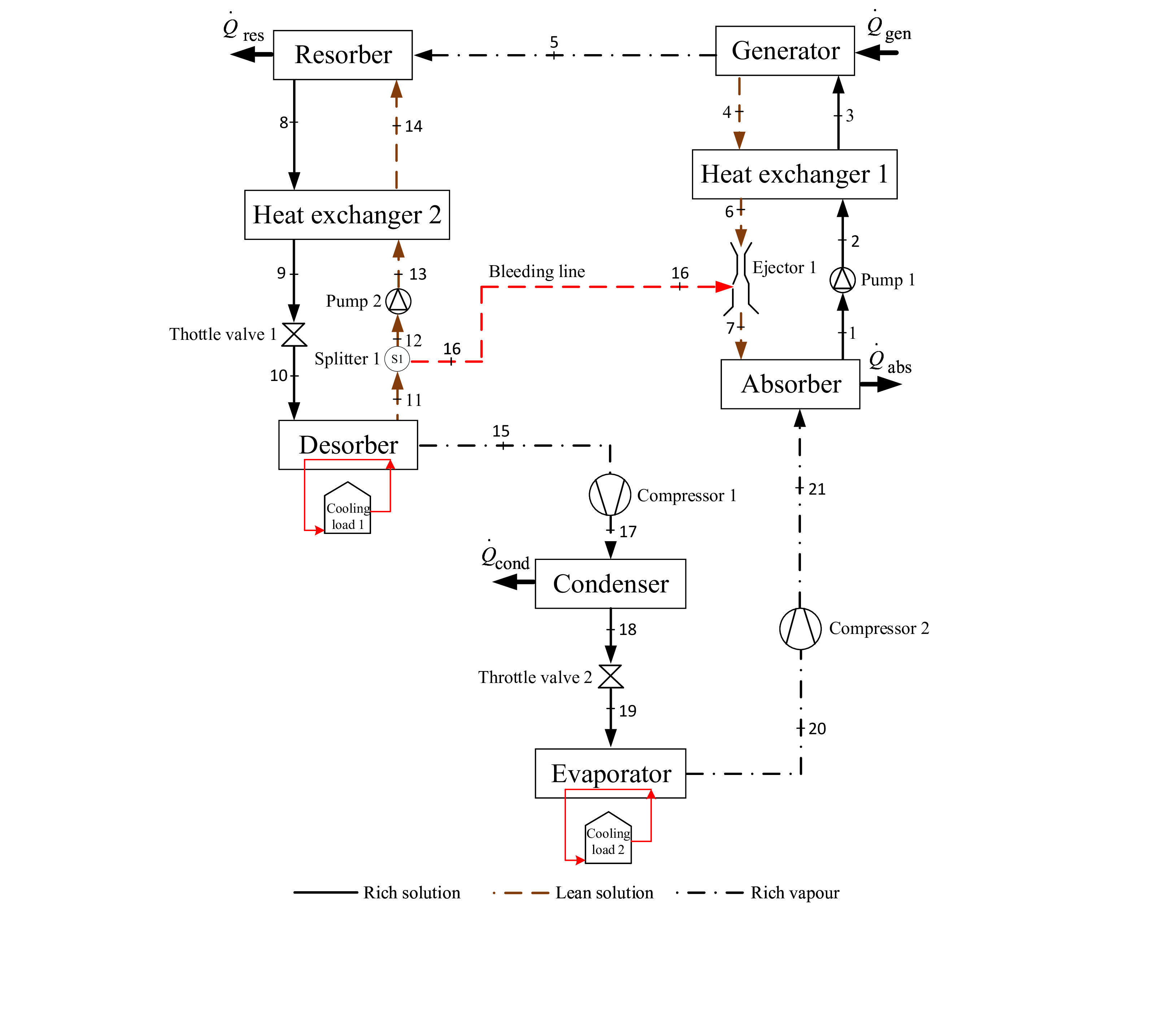
The Ejector Assisted Compression-Absorption-Resorption (ECAR) cooling cycle presents an innovative solution to address the escalating energy demand and CO2 emissions from traditional refrigeration and air conditioning systems. By utilizing low-grade energy sources such as waste heat or renewable heat, this cycle offers higher efficiency and reduced electricity consumption compared to conventional vapor compression systems.
Cooling is essential in modern life, consuming 17% of the world's generated electricity. Traditional vapour compression systems are energy-intensive, with the mechanical compressor alone consumes about 70% of the input electricity. This results in higher CO2, especially from coal-based electricity generation. There is a need for more efficient, low-cost, heat-driven cooling technologies to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
- This innovation enables dual refrigerating effects at different temperatures, and is suitable for both space cooling and cold storage/refrigeration.
- The technology utilizes a zeotropic mixture as the refrigerant for enhanced flexibility in operating pressures and temperatures.
- It integrates an ejector in the absorption circuit to improve efficiency by replacing certain components like expansion valves.
- It is able to operate at lower cycle pressures and achieve higher Coefficient Of Performance (COP) compared to conventional systems.
- Significant energy savings of 30% to 60% are achievable, particularly when utilizing industrial waste heat.
- It has compact design and lower heat source temperature requirements as compared to double-effect Vapour Absorption-Resorption Cycle (VARC) systems, which optimizes performance.
The system configurations were simulated and validated, with results compared to the state-of-the-art literature in experimental and simulation studies. The prototype has not been fabricated and tested because most of the components are off-the-shelf, and the scale of testing requires industrial support and funding.
The Ejector Assisted Compression-Absorption-Resorption (ECAR) cooling cycle is a conceptual innovation and research and development are ongoing to refine the design and optimize performance parameters.
3
The ECAR cooling cycle has the potential to significantly reduce energy consumption and CO2 emissions associated with cooling systems, contributing to sustainability goals and reducing environmental impact. It also offers economic benefits through energy savings and potential utilization of waste heat in industries.
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) industry:
- Commercial, and industrial refrigeration for space cooling and thermal processes
- Cold storage and refrigeration applications
- Utilization of waste heat in various industries for cooling purposes
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202121037660
509335