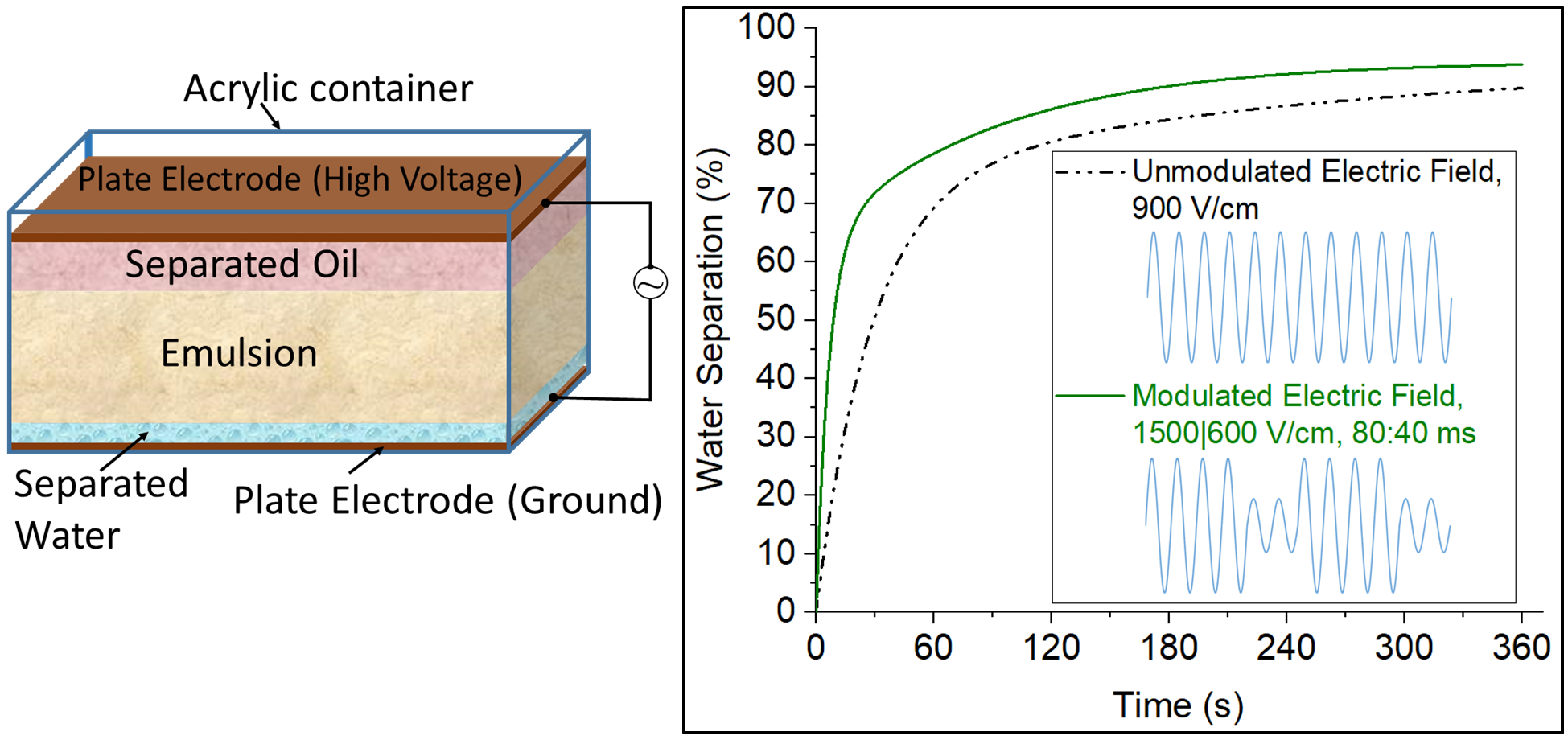
The present invention describes a method for separating water from a water-in-oil emulsion. This method involves applying an electric field to the emulsion using a pair of electrodes, promoting coalescence and facilitating the rapid formation of larger droplets, which can then be used to effectively separate the water-in-oil emulsion due to gravity.
Crude oil naturally exists as a water-in-oil emulsion, requiring processing before refining, with one essential step being the separation of water from the crude oil. This separation process also offers the additional benefit of removing dissolved salt from the crude oil. Therefore, dehydrating and desalting crude oil is highly advantageous. Consequently, there is a demand for an optimized method of applying an electrical field to emulsions to achieve efficient water separation from water-in-oil emulsions.
- Applied electric field undergoes modulation between a higher first electric field and a lower second electric field.
- The higher electric field helps in fastening the rate of approach of the drops.
- The second electric field promotes the coalescence of these closely positioned droplets into larger water droplets.
- It enhances coalescence, facilitating the rapid formation of larger droplets.
- It achieves accelerated coalescence of water droplets, leading to quicker separation of water from water-in-oil emulsions.
A voltage modulation technique uses the high electric fields to concentrate droplets and low fields to coalesce them. This involves the alternating application of low and high sinusoidal AC fields for varying durations, with a 1/2 duty cycle. The optimal modulation frequency for alternating these fields is 10 Hz, while the optimal frequency for the sinusoidal AC fields is found to be 50 Hz. This technique achieves a significantly higher separation rate compared to the non-modulated approach, with optimized values for both high and low electric fields.
An efficient and optimised electric waveform has been identified and demonstrated through experiments to yield higher separation of water-in-oil emulsions for different types of electrocoalescers.
4
This innovation could be useful in significant intensification of dehydration and desalting processes.
Electrocoalescers are widely used and have tremendous applications in crude oil industry.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202121053365
400352