The present invention outlines a method for fabricating poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) (PEVA-SUN), intended for use as an encapsulant sheet in the photovoltaic (PV) industry. This invention challenges the conventional approach in the PV industry, which typically uses EVA sheets with a VA content between 28% to 33%.
Instead, this method recommends utilizing a VA content of 19%-21% for the front side encapsulation and 21%-23% for the back side encapsulation in the PEVA copolymer.
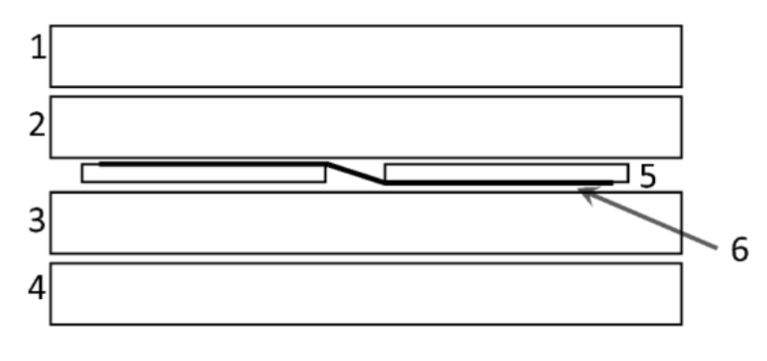
Figure: Architecture of a PV module that contains PEVA-SUN encapsulant sheets containing 19%-21% VA content in the front (2) and 21-23% VA content in the back-side sheet (3). The front layer is a glass (1) that faces the sunny side, while a polymeric backsheet (4) is used on the backside of the modules. Interconnected solar cells (5, 6) are placed between front PEVA-SUN and back PEVA-SUN sheets.
Poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) (PEVA) is a widely used material for encapsulating solar cells in photovoltaic modules. However, during service, PEVA films are prone to degradation due to exposure to environmental stressors like humidity, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and temperature fluctuations. These stressors cause the vinyl acetate in PEVA to degrade, leading to the formation of volatile compounds such as acetic acid, lactones, ketones, and acetaldehyde.
- This innovation reduces the vinyl acetate (VA) content to 19%-21% and 21%-23% by weight in the PEVA copolymer for the front and back side encapsulation.
- The front layer encapsulation film has lower vinyl-acetate content than the back layer encapsulation film.
- It increases the stability of the encapsulation sheet against the environmental stressors.
- It reduces the manufacturing cost.
A solar cell module comprising:
- A top glass layer that faces the outer atmosphere.
- A front layer encapsulation film made of a thin film with 19% to 21% by weight of vinyl acetate and additives, positioned above the solar cells and below the glass layer.
- A plurality of solar cells connected with multiple cell interconnects.
- A back layer encapsulation film made of a thin film with 21% to 23% by weight of vinyl acetate and additives, positioned below the solar cells.
- A backsheet positioned below the back layer encapsulation film.
- The solar cells are encapsulated between the front and back encapsulation films.
Both encapsulation films include the following additives:
- 1.6% by weight of 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-di(tert-butylperoxyl)-hexane
- 0.25% by weight of UV absorber (2-Hydroxy-4-(acetyloxy) benzophenone)
- 0.2% by weight of bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl) sebacate
- 0.45% by weight of vinyltrimethoxysilane coupling agent
The invention is currently at the stage of concept development.
4
The invention enhances the quality of solar panels while also decreasing the cost required. This makes solar energy more accessible and affordable for the public and will help in increasing green energy consumption.
In the photovoltaic (PV) industry PEVA copolymer is used for manufacturing of encapsulation of solar cells in a solar module. The invention reduces manufacturing cost and increases stability making it extremely useful for the PV industry.
Geography of IP
Type of IP
202321000655
466932