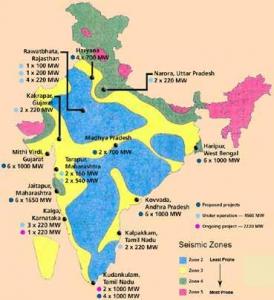
India is looking towards nuclear power as a viable clean energy option to meet its growing energy demands. A target has been set in India’s climate action plan to increase the current capacity of nuclear power from 5 - 63 GW. However, concerns related to seismic safety of nuclear power plants (NPPs) first need to be addressed. One of the possible mitigation measures could be to use seismic isolation to reduce the seismic risk to NPPs. Seismic (base) isolation is a passive control device which reduces damaging effects of earthquakes on a structure through isolators installed between foundation and the superstructure. A particular family of seismic isolators are elastomeric bearings, which are constructed using alternate layers of rubber and steel shims. The high vertical stiffness of these bearings provide stability. The horizontal flexibility provides isolation of the structure from ground shaking, essentially reducing deformation and force demands in the superstructure.The current challenges lie in ensuring robust performance of seismic isolators under extreme earthquakes and reliable prediction of numerical response. This requires testing under representative loading and development of robust computational tools. A major challenge in adoption of these systems in India are the lack of their analysis and design guidelines compatible with Indian seismic analysis and design codes. This research addresses these issues to ensure seismic safety of nuclear structure using base isolators.
Prof. Manish Kumar
